Page 460 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 460
444 M. WEKK AND 1 AKTAA
The observation area is a 25 mm wide cylindrical zone in the middle of the specimen, where
the stress distribution is nearly homogeneous. As an advantage compared to a fully cylindrical
specimen, this specimen is less susceptible to buckling and the most probable location of crack
nucleation, the middle of the specimen, is restricted considerably. Thus, measurement of the
radial extensometers near the location of crack nucleation is ensured. In addition, there are not
any sharp changes of the outline, which could provoke notch effects, due to the geometry
chosen.
The chosen material for this tests was the high-alloy stainless steel X2CrNiMoN1712 ( German
standard 1.4909, American standard AIS1 316 L (N)). This material is in discussion for the first
wall of a fusion reactor.
The specimens were made out of seamless and textureless tubes. After the turning of the
specimens the surface of the measurement area were fine ground. The chemical composition
and the basic material properties are shown in table 1 and table 2.
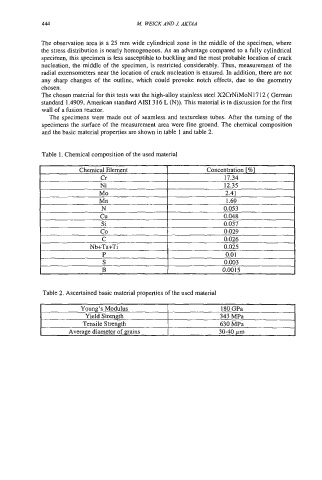
Table 1. Chemical composition of the used material
Table 2. Ascertained basic material properties of the used material
Youna’s Modulus 1 a0 GPa
Yield Strength 343 MPa
Tensile Strength 630 MPa
Average diameter of grains 30-40 pm