Page 84 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 84
Micro-Crack Growth Behavior in Weldments of a Nickel-Base Superalloy Under .__ 69
Crack Growth Behavior
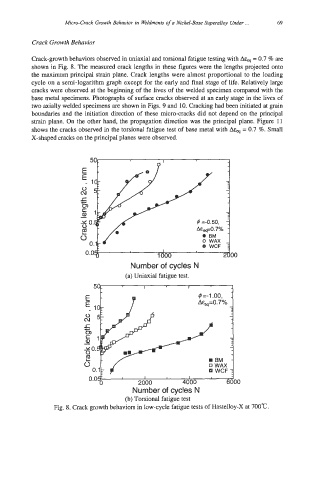
Crack-growth behaviors observed in uniaxial and torsional fatigue testing with Ah = 0.7 % are
shown in Fig. 8. The measured crack lengths in these figures were the lengths projected onto
the maximum principal strain plane. Crack lengths were almost proportional to the loading
cycle on a semi-logarithm graph except for the early and final stage of life. Relatively large
cracks were observed at the beginning of the lives of the welded specimen compared with the
base metal specimens. Photographs of surface cracks observed at an early stage in the lives of
two axially welded specimens are shown in Figs. 9 and 10. Cracking had been initiated at grain
boundaries and the initiation direction of these micro-cracks did not depend on the principal
strain plane. On the other hand, the propagation direction was the principal plane. Figure 11
shows the cracks observed in the torsional fatigue test of base metal with Ah = 0.7 %. Small
X-shaped cracks on the principal planes were observed.
Fig. 8. at 700°C.