Page 208 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 208
8.5 Application of HIFU on thermal ablation 207
therapies. Destruction of vascular thrombosis, which is the cause of ischemic stroke
using ultrasound waves is called sonothrombolysis. However, ultrasound alone is
also capable for sonothrombolysis, but the cavitation due to microbubble enhances
the efficacy. High-energy and low-energy ultrasound are used to create sonothrom-
bolysis targeted to monitor the microbubbles due to cavitation into the region of
thrombosis, respectively [88]. Also, microbubbles are more capable of holding gases
like oxygen and can be used to deliver oxygen. it carries more oxygen as compared
to other vehicles and liquid.
8.5 Application of HIFU on thermal ablation
HIFU is widely used in thermal cancer therapy. During sonication, temperature
increases in tissues and secondary flow streams in vessels. Tissue temperature rise
and blood acoustic streaming mostly depend on ultrasonic field characteristics such
as intensity, frequency and pulse duration. In this example, temperature rise due to
high intensity focused ultrasonic beams which yields to necrosis of cancerous cells is
numerically studied. Solving nonlinear acoustofluidics, second-order of perturbation
theory is applied to continuity, momentum, energy, and state equations.
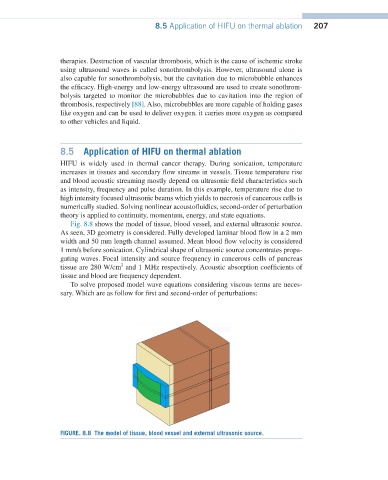
Fig. 8.8 shows the model of tissue, blood vessel, and external ultrasonic source.
As seen, 3D geometry is considered. Fully developed laminar blood flow in a 2 mm
width and 50 mm length channel assumed. Mean blood flow velocity is considered
1 mm/s before sonication. Cylindrical shape of ultrasonic source concentrates propa-
gating waves. Focal intensity and source frequency in cancerous cells of pancreas
2
tissue are 280 W/cm and 1 MHz respectively. Acoustic absorption coefficients of
tissue and blood are frequency dependent.
To solve proposed model wave equations considering viscous terms are neces-
sary. Which are as follow for first and second-order of perturbations:
FIGURE. 8.8 The model of tissue, blood vessel and external ultrasonic source.