Page 222 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 222
9.1 Introduction 221
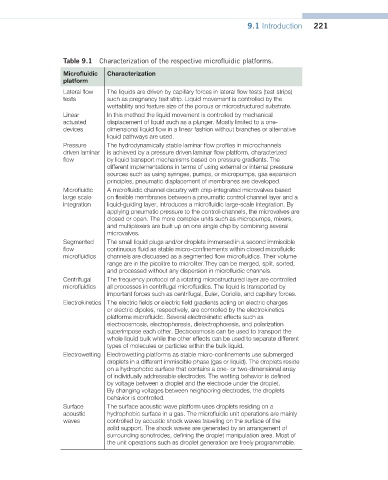
Table 9.1 Characterization of the respective microfluidic platforms.
Microfluidic Characterization
platform
Lateral flow The liquids are driven by capillary forces in lateral flow tests (test strips)
tests such as pregnancy test strip. Liquid movement is controlled by the
wettability and feature size of the porous or microstructured substrate.
Linear In this method the liquid movement is controlled by mechanical
actuated displacement of liquid such as a plunger. Mostly limited to a one-
devices dimensional liquid flow in a linear fashion without branches or alternative
liquid pathways are used.
Pressure The hydrodynamically stable laminar flow profiles in microchannels
driven laminar is achieved by a pressure driven laminar flow platform, characterized
flow by liquid transport mechanisms based on pressure gradients. The
different implementations in terms of using external or internal pressure
sources such as using syringes, pumps, or micropumps, gas expansion
principles, pneumatic displacement of membranes are developed.
Microfluidic A microfluidic channel circuitry with chip-integrated microvalves based
large scale on flexible membranes between a pneumatic control channel layer and a
integration liquid-guiding layer, introduces a microfluidic large-scale integration. By
applying pneumatic pressure to the control-channels, the microvalves are
closed or open. The more complex units such as micropumps, mixers,
and multiplexers are built up on one single chip by combining several
microvalves.
Segmented The small liquid plugs and/or droplets immersed in a second immiscible
flow continuous fluid as stable micro-confinements within closed microfluidic
microfluidics channels are discussed as a segmented flow microfluidics. Their volume
range are in the picolitre to microliter.They can be merged, split, sorted,
and processed without any dispersion in microfluidic channels.
Centrifugal The frequency protocol of a rotating microstructured layer are controlled
microfluidics all processes in centrifugal microfluidics. The liquid is transported by
important forces such as centrifugal, Euler, Coriolis, and capillary forces.
Electrokinetics The electric fields or electric field gradients acting on electric charges
or electric dipoles, respectively, are controlled by the electrokinetics
platforms microfluidic. Several electrokinetic effects such as
electroosmosis, electrophoresis, dielectrophoresis, and polarization
superimpose each other. Electroosmosis can be used to transport the
whole liquid bulk while the other effects can be used to separate different
types of molecules or particles within the bulk liquid.
Electrowetting Electrowetting platforms as stable micro-confinements use submerged
droplets in a different immiscible phase (gas or liquid). The droplets reside
on a hydrophobic surface that contains a one- or two-dimensional array
of individually addressable electrodes. The wetting behavior is defined
by voltage between a droplet and the electrode under the droplet.
By changing voltages between neighboring electrodes, the droplets
behavior is controlled.
Surface The surface acoustic wave platform uses droplets residing on a
acoustic hydrophobic surface in a gas. The microfluidic unit operations are mainly
waves controlled by acoustic shock waves traveling on the surface of the
solid support. The shock waves are generated by an arrangement of
surrounding sonotrodes, defining the droplet manipulation area. Most of
the unit operations such as droplet generation are freely programmable.