Page 246 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 246
References 245
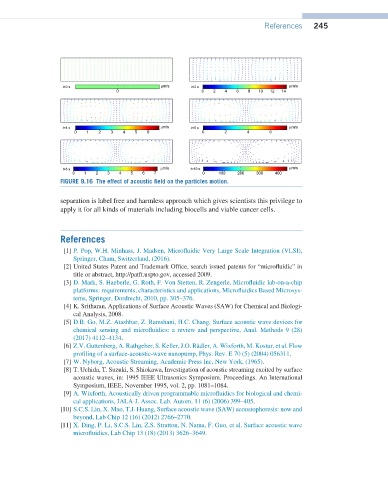
FIGURE 9.16 The effect of acoustic field on the particles motion.
separation is label free and harmless approach which gives scientists this privilege to
apply it for all kinds of materials including biocells and viable cancer cells.
References
[1] P. Pop, W.H. Minhass, J. Madsen, Microfluidic Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI),
Springer, Cham, Switzerland, (2016).
[2] United States Patent and Trademark Office, search issued patents for “microfluidic” in
title or abstract, http://patft.uspto.gov, accessed 2009.
[3] D. Mark, S. Haeberle, G. Roth, F. Von Stetten, R. Zengerle, Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip
platforms: requirements, characteristics and applications, Microfluidics Based Microsys-
tems, Springer, Dordrecht, 2010, pp. 305–376.
[4] K. Sritharan, Applications of Surface Acoustic Waves (SAW) for Chemical and Biologi-
cal Analysis, 2008.
[5] D.B. Go, M.Z. Atashbar, Z. Ramshani, H.C. Chang, Surface acoustic wave devices for
chemical sensing and microfluidics: a review and perspective, Anal. Methods 9 (28)
(2017) 4112–4134.
[6] Z.V. Guttenberg, A. Rathgeber, S. Keller, J.O. Rädler, A. Wixforth, M. Kostur, et al. Flow
profiling of a surface-acoustic-wave nanopump, Phys. Rev. E 70 (5) (2004) 056311.
[7] W. Nyborg, Acoustic Streaming, Academic Press Inc, New York, (1965).
[8] T. Uchida, T. Suzuki, S. Shiokawa, Investigation of acoustic streaming excited by surface
acoustic waves, in: 1995 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium. Proceedings. An International
Symposium, IEEE, November 1995, vol. 2, pp. 1081–1084.
[9] A. Wixforth, Acoustically driven programmable microfluidics for biological and chemi-
cal applications, JALA-J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 11 (6) (2006) 399–405.
[10] S.C.S. Lin, X. Mao, T.J. Huang, Surface acoustic wave (SAW) acoustophoresis: now and
beyond, Lab Chip 12 (16) (2012) 2766–2770.
[11] X. Ding, P. Li, S.C.S. Lin, Z.S. Stratton, N. Nama, F. Guo, et al. Surface acoustic wave
microfluidics, Lab Chip 13 (18) (2013) 3626–3649.