Page 274 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 274
250 11 Nitrile Converting Enzymes Involved in Natural and Synthetic Cascade Reactions
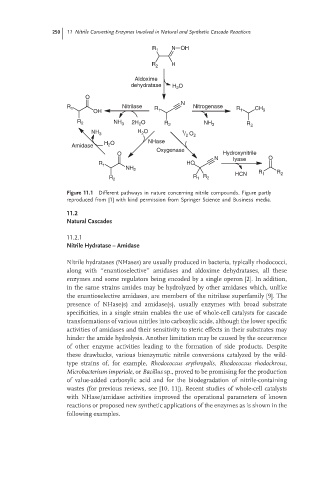
R 1 N OH
R 2 H
Aldoxime
dehydratase H O
2
O
N
R 1 Nitrilase R Nitrogenase R CH
OH 1 1 3
R 2 NH 3 2H 2 O R 2 NH 3 R 2
H 2 O 1
NH 3 / O 2
2
Amidase H 2 O NHase
Oxygenase
O Hydroxynitrile
N lyase O
R 1 HO
NH 2
R R HCN R 1 R 2
R 2 1 2
Figure 11.1 Different pathways in nature concerning nitrile compounds. Figure partly
reproduced from [1] with kind permission from Springer Science and Business media.
11.2
Natural Cascades
11.2.1
Nitrile Hydratase – Amidase
Nitrile hydratases (NHases) are usually produced in bacteria, typically rhodococci,
along with ‘‘enantioselective’’ amidases and aldoxime dehydratases, all these
enzymes and some regulators being encoded by a single operon [2]. In addition,
in the same strains amides may be hydrolyzed by other amidases which, unlike
the enantioselective amidases, are members of the nitrilase superfamily [9]. The
presence of NHase(s) and amidase(s), usually enzymes with broad substrate
specificities, in a single strain enables the use of whole-cell catalysts for cascade
transformations of various nitriles into carboxylic acids, although the lower specific
activities of amidases and their sensitivity to steric effects in their substrates may
hinder the amide hydrolysis. Another limitation may be caused by the occurrence
of other enzyme activities leading to the formation of side products. Despite
these drawbacks, various bienzymatic nitrile conversions catalyzed by the wild-
type strains of, for example, Rhodococcus erythropolis, Rhodococcus rhodochrous,
Microbacterium imperiale,or Bacillus sp., proved to be promising for the production
of value-added carboxylic acid and for the biodegradation of nitrile-containing
wastes (for previous reviews, see [10, 11]). Recent studies of whole-cell catalysts
with NHase/amidase activities improved the operational parameters of known
reactions or proposed new synthetic applications of the enzymes as is shown in the
following examples.