Page 365 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 365
16.2 Iminocyclitol and Aminocyclitol Synthesis 341
good donors for aldolases [14]. The Cbz moiety is a widely used amino pro-
tecting group in peptide chemistry, employed in many orthogonal protection
schemes, and its deprotection takes place under the same reaction conditions
as the reductive amination and therefore both reactions can be readily per-
formed catalytically in one pot. Furthermore, N-protected aminoaldehydes have the
tremendous advantage that they can be easily obtained from the wide structural
variety of readily available optically pure α-or β-amino acids or alcohols and their
derivatives [15].
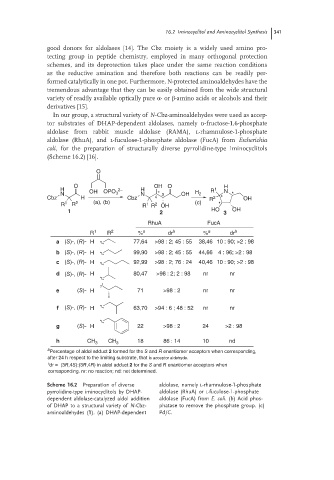
In our group, a structural variety of N-Cbz-aminoaldehydes were used as accep-
tor substrates of DHAP-dependent aldolases, namely d-fructose-1,6-phosphate
aldolase from rabbit muscle aldolase (RAMA), l-rhamnulose-1-phosphate
aldolase (RhuA), and l-fuculose-1-phosphate aldolase (FucA) from Escherichia
coli, for the preparation of structurally diverse pyrrolidine-type iminocyclitols
(Scheme 16.2) [16].
O
O OH O H
H OH OPO 2− H R 1 N
N 3 N * 3 OH H 2 *
Cbz H Cbz 4 R 2 * OH
R 1 R 2 (a), (b) R R 2 OH (c) *
1
1 2 HO 3 OH
RhuA FucA
R 1 R 2 % a dr b % a dr b
a (S)-, (R)- H 77,64 >98 : 2; 45 : 55 38,46 10 : 90; >2 : 98
b (S)-, (R)- H 99,90 >98 : 2; 45 : 55 44,66 4 : 96; >2 : 98
c (S)-, (R)- H 92,99 >98 : 2; 76 : 24 40,46 10 : 90; >2 : 98
d (S)-, (R)- H 80,47 >98 : 2; 2 : 98 nr nr
e (S)- H 71 >98 : 2 nr nr
f (S)-, (R)- H 63,70 >94 : 6 ; 48 : 52 nr nr
g (S)- H 22 >98 : 2 24 >2 : 98
h CH 3 CH 3 18 86 : 14 10 nd
a
Percentage of aldol adduct 2 formed for the S and R enantiomer acceptors when corresponding,
after 24 h respect to the limiting substrate, that is acceptor aldehyde.
b
dr = (3R,4S):(3R,4R) in aldol adduct 2 for the S and R enantiomer acceptors when
corresponding. nr: no reaction; nd: not determined.
Scheme 16.2 Preparation of diverse aldolase, namely L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate
pyrrolidine-type iminocyclitols by DHAP- aldolase (RhuA) or L-fuculose-1-phosphate
dependent aldolase-catalyzed aldol addition aldolase (FucA) from E. coli. (b) Acid phos-
of DHAP to a structural variety of N-Cbz- phatase to remove the phosphate group. (c)
aminoaldehydes (1). (a) DHAP-dependent Pd/C.