Page 364 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 364
340 16 Aldolases as Catalyst for the Synthesis of Carbohydrates and Analogs
such as iminocyclitols, aminocyclitols, and deoxysugars. Imino and aminocyclitols
are naturally occurring sugar analogs [7], many of them being potent inhibitors of
glycosidases and glycosyltransferases [8]. By virtue of these inhibitory properties,
they have attracted much interest as potential therapeutic agents because they
can modulate the metabolism of oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates (i.e., gly-
colipids and glycoproteins), molecules of paramount importance in biochemical
recognition processes such as cellular adhesion, viral infections, cellular differ-
entiation, metastasis, and numerous signal transduction events [9]. Furthermore,
they are useful probes in fundamental biochemical studies of the glycosidase
mechanism [10].
Another large group of carbohydrate analogs consists of deoxysugars, which
often play a crucial role as recognition elements in bioactive molecules [11].
Deoxysugars can usually be found as conjugates with natural products along with
other carbohydrates in polysaccharide structures [12]. The role that they play in
many physiological processes is attributed in part to the enhanced hydrophobicity
displayed with respect to the fully oxygenated analogs [12a, 13].
Here we recount the latest research on chemoenzymatic multistep and cascade
strategies for the synthesis of iminocyclitols, carbohydrates, and deoxysugars
from N-protected aminoaldehydes, hydroxyaldehydes, and simple alkylaldehydes,
respectively. The key step in all of them is the stereoselective aldol addition reaction
of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and its unphosphorylated analogs to the
acceptor aldehydes using DHAP-dependent and dihydroxyacetone- (DHA)-utilizing
aldolases, respectively, as biocatalysts.
16.2
Iminocyclitol and Aminocyclitol Synthesis
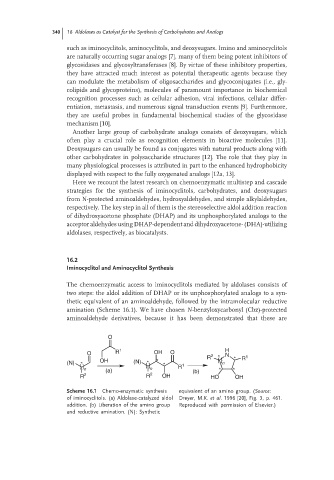
The chemoenzymatic access to iminocyclitols mediated by aldolases consists of
two steps: the aldol addition of DHAP or its unphosphorylated analogs to a syn-
thetic equivalent of an aminoaldehyde, followed by the intramolecular reductive
amination (Scheme 16.1). We have chosen N-benzyloxycarbonyl (Cbz)-protected
aminoaldehyde derivatives, because it has been demonstrated that these are
O
O R 1 OH O H
N
R 2 * * R 1
(N) * OH (N) * * * 1 n
n (a) n R (b) * *
R 2 R 2 OH HO OH
Scheme 16.1 Chemo-enzymatic synthesis equivalent of an amino group. (Source:
of iminocyclitols. (a) Aldolase-catalyzed aldol Dreyer, M.K. et al. 1996 [20], Fig. 3, p. 461.
addition. (b) Liberation of the amino group Reproduced with permission of Elsevier.)
and reductive amination. (N): Synthetic