Page 418 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 418
394 18 Methyltransferases in Biocatalysis
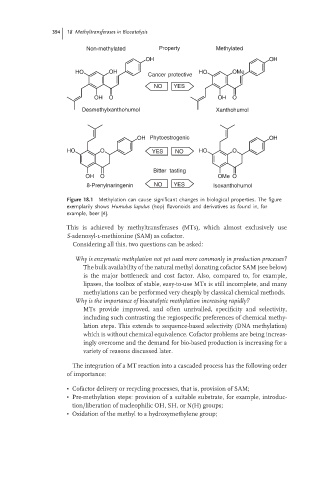
Non-methylated Property Methylated
OH OH
HO OH HO OMe
Cancer protective
NO YES
OH O OH O
Desmethylxanthohumol Xanthohumol
OH Phytoestrogenic OH
HO O YES NO HO O
Bitter tasting
OH O OMe O
8-Prenylnaringenin NO YES Isoxanthohumol
Figure 18.1 Methylation can cause significant changes in biological properties. The figure
exemplarily shows Humulus lupulus (hop) flavonoids and derivatives as found in, for
example, beer [4].
This is achieved by methyltransferases (MTs), which almost exclusively use
S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM) as cofactor.
Considering all this, two questions can be asked:
Why is enzymatic methylation not yet used more commonly in production processes?
The bulk availability of the natural methyl donating cofactor SAM (see below)
is the major bottleneck and cost factor. Also, compared to, for example,
lipases, the toolbox of stable, easy-to-use MTs is still incomplete, and many
methylations can be performed very cheaply by classical chemical methods.
Why is the importance of biocatalytic methylation increasing rapidly?
MTs provide improved, and often unrivalled, specificity and selectivity,
including such contrasting the regiospecific preferences of chemical methy-
lation steps. This extends to sequence-based selectivity (DNA methylation)
which is without chemical equivalence. Cofactor problems are being increas-
ingly overcome and the demand for bio-based production is increasing for a
variety of reasons discussed later.
The integration of a MT reaction into a cascaded process has the following order
of importance:
• Cofactor delivery or recycling processes, that is, provision of SAM;
• Pre-methylation steps: provision of a suitable substrate, for example, introduc-
tion/liberation of nucleophilic OH, SH, or N(H) groups;
• Oxidation of the methyl to a hydroxymethylene group;