Page 60 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 60
36 2 New Trends in the In Situ Enzymatic Recycling of NAD(P)(H) Cofactors
HO OH
NAD(P) + Substrate red
O 2
Radical O O Ct-XR Dehydrogenase
reaction
NAD(P)H
H 2 O 2 Product ox
(a)
OH
OCH 3 + Substrate
O 2 NAD(P) red
CO
H 3
OH
Laccase Ml-LPD Dehydrogenase
O
OCH 3
H 2 O NAD(P)H Product ox
H 3 CO
O
(b)
H
N
O 2 NAD(P) + Substrate red
O N(CH 3 2
)
Laccase Dehydrogenase
N
H O NAD(P)H Product
2
+ ox
O N(CH 3 ) 2
(c)
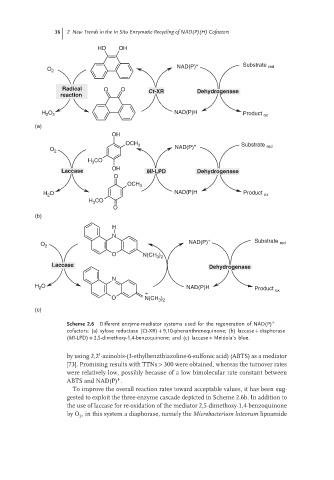
Scheme 2.6 Different enzyme-mediator systems used for the regeneration of NAD(P) +
cofactors: (a) xylose reductase (Ct-XR) + 9,10-phenanthrenequinone; (b) laccase + diaphorase
(Ml-LPD) + 2,5-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone; and (c) laccase + Meldola’s blue.
′
by using 2,2 -azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) as a mediator
[73]. Promising results with TTNs > 300 were obtained, whereas the turnover rates
were relatively low, possibly because of a low bimolecular rate constant between
+
ABTS and NAD(P) .
To improve the overall reaction rates toward acceptable values, it has been sug-
gested to exploit the three-enzyme cascade depicted in Scheme 2.6b. In addition to
the use of laccase for re-oxidation of the mediator 2,5-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone
by O , in this system a diaphorase, namely the Microbacterium luteorum lipoamide
2