Page 126 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 126
104 4 Synthesis, Properties, and Mathematical Modeling of Biodegradable Aliphatic Polyesters
PPSu
T210
T220
T230
COOH (eq/10 6 g)
T245
100
10
0 50 100 150 200
(a)
Polycondensation time (min)
PPSu
210 °C
Hydroxyl content (eq/10 6 g) 245 °C
220 °C
1000
230 °C
100
0 50 100 150 200
(b) Polycondensation time (min)
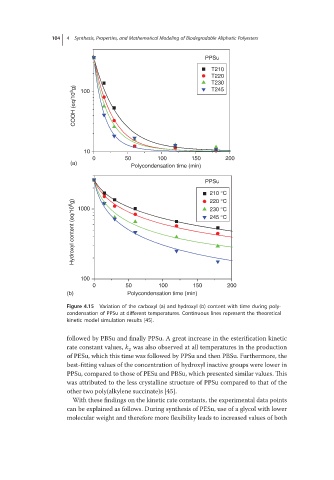
Figure 4.15 Variation of the carboxyl (a) and hydroxyl (b) content with time during poly-
condensation of PPSu at different temperatures. Continuous lines represent the theoretical
kinetic model simulation results [45].
followed by PBSu and finally PPSu. A great increase in the esterification kinetic
rate constant values, k was also observed at all temperatures in the production
2
of PESu, which this time was followed by PPSu and then PBSu. Furthermore, the
best-fitting values of the concentration of hydroxyl inactive groups were lower in
PPSu,comparedtothose of PESu andPBSu, whichpresented similarvalues.This
was attributed to the less crystalline structure of PPSu compared to that of the
other two poly(alkylene succinate)s [45].
With these findings on the kinetic rate constants, the experimental data points
can be explained as follows. During synthesis of PESu, use of a glycol with lower
molecular weight and therefore more flexibility leads to increased values of both