Page 249 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 249
9.4 Mechanism of Nano-Morphology Formation 227
Obviously, the hydrogen bonding is a powerful tool for controlling the proper-
ties of polymer blends, and more specifically the nano-morphology when convert-
ing the bulk polymers into nano-sized materials. Blending completely immiscible
polymers and applying the MFC concept makes possible the isolation of nano-
sized material in the form of individual not interconnected nanofibrils. In contrast
to this situation, dealing with blend partners inclined to formation of hydrogen
bonds and thus converting the blend into a partially miscible one, the final nano-
sized material is a nanofibrillar nanoporous 3-D network.
9.4
Mechanism of Nano-Morphology Formation in Polymer Blends without and with
Hydrogen Bonding
In addition to the outlined morphological difference between the two types of
polymer blends, without and with hydrogen bonding between the blend partners,
it turned out that the mechanism of formation of the nano-sized materials is com-
pletely different for the one or the other case. Detailed studies on the mechanism
of formation of the individual micro- and nanofibrils led to the conclusion that it
takes place during the cold drawing via coalescence of the elongated droplets [18],
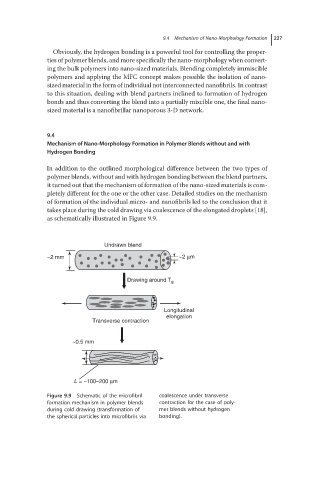
as schematically illustrated in Figure 9.9.
Undrawn blend
~2 mm ~2 μm
Drawing around T g
Longitudinal
elongation
Transverse contraction
~0.5 mm
L = ~100–200 μm
Figure 9.9 Schematic of the microfibril coalescence under transverse
formation mechanism in polymer blends contraction for the case of poly-
during cold drawing (transformation of mer blends without hydrogen
the spherical particles into microfibrils via bonding).