Page 97 - Biofuels for a More Sustainable Future
P. 97
Indicators for sustainability assessment 87
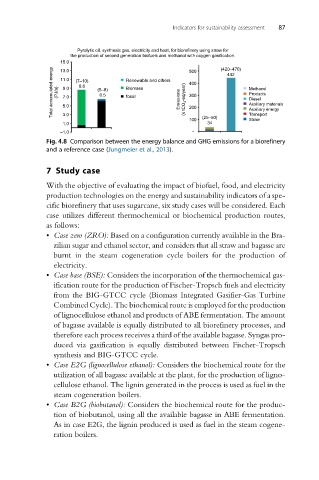
Pyrolytic oil, synthesis gas, electricity and heat, for biorefinery using straw for
the production of second generation biofuels and methanol with oxygen gasification.
15.0 500 (420–470)
Total accumulated energy (PJ/a) 11.0 (7–10) (5–8) Renewable and others Emissions (k tCO 2 -eq/year) 400 Methanol
13.0
442
8.6
Biomass
9.0
Products
6.5
300
fossil
7.0
Diesel
Auxiliary materials
5.0
200
Transport
3.0
100 (25–50) Auxiliary energy
Straw
1.0 34
–1.0 -
Fig. 4.8 Comparison between the energy balance and GHG emissions for a biorefinery
and a reference case (Jungmeier et al., 2013).
7Study case
With the objective of evaluating the impact of biofuel, food, and electricity
production technologies on the energy and sustainability indicators of a spe-
cific biorefinery that uses sugarcane, six study cases will be considered. Each
case utilizes different thermochemical or biochemical production routes,
as follows:
• Case zero (ZRO): Based on a configuration currently available in the Bra-
zilian sugar and ethanol sector, and considers that all straw and bagasse are
burnt in the steam cogeneration cycle boilers for the production of
electricity.
• Case base (BSE): Considers the incorporation of the thermochemical gas-
ification route for the production of Fischer-Tropsch fuels and electricity
from the BIG-GTCC cycle (Biomass Integrated Gasifier-Gas Turbine
Combined Cycle). The biochemical route is employed for the production
of lignocellulose ethanol and products of ABE fermentation. The amount
of bagasse available is equally distributed to all biorefinery processes, and
therefore each process receives a third of the available bagasse. Syngas pro-
duced via gasification is equally distributed between Fischer-Tropsch
synthesis and BIG-GTCC cycle.
• Case E2G (lignocellulose ethanol): Considers the biochemical route for the
utilization of all bagasse available at the plant, for the production of ligno-
cellulose ethanol. The lignin generated in the process is used as fuel in the
steam cogeneration boilers.
• Case B2G (biobutanol): Considers the biochemical route for the produc-
tion of biobutanol, using all the available bagasse in ABE fermentation.
As in case E2G, the lignin produced is used as fuel in the steam cogene-
ration boilers.