Page 180 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 180
BIOMECHANICS OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 157
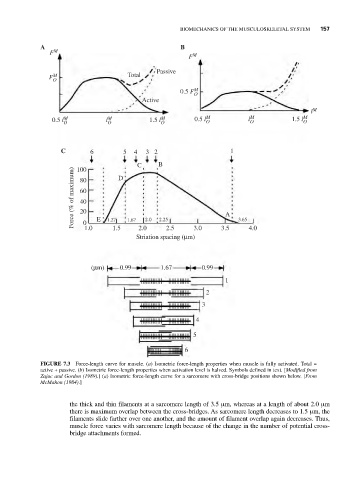
A B
F M M
F
Passive
F M Total
O
0.5 F M
O
Active
l M
0.5 l M l M 1.5 l M 0.5 l M l M 1.5 l M
O O O O O O
C 6 5 4 3 2 1
C B
100
Force (% of maximum) 60 A
D
80
40
20
E
2.0
2.25
1.67
1.27
0
2.0
2.5
1.0
1.5
Striation spacing (μm) 3.0 3.5 3.65 4.0
(μm) 0.99 1.67 0.99
1
2
3
4
5
6
FIGURE 7.3 Force-length curve for muscle. (a) Isometric force-length properties when muscle is fully activated. Total =
active + passive. (b) Isometric force-length properties when activation level is halved. Symbols defined in text. [Modified from
Zajac and Gordon (1989).] (a) Isometric force-length curve for a sarcomere with cross-bridge positions shown below. [From
McMahon (1984).]
the thick and thin filaments at a sarcomere length of 3.5 μm, whereas at a length of about 2.0 μm
there is maximum overlap between the cross-bridges. As sarcomere length decreases to 1.5 μm, the
filaments slide farther over one another, and the amount of filament overlap again decreases. Thus,
muscle force varies with sarcomere length because of the change in the number of potential cross-
bridge attachments formed.