Page 312 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 312
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AS A TOOL TO ESTIMATE MUSCLE FORCES 289
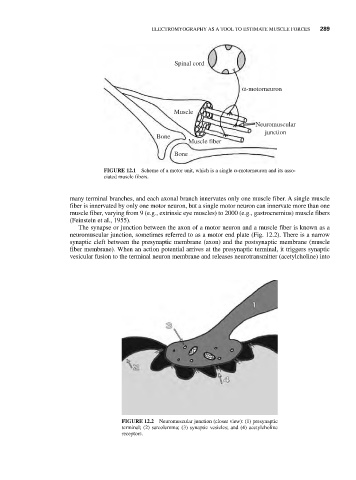
Spinal cord
α-motorneuron
Muscle
Neuromuscular
junction
Bone
Muscle fiber
Bone
FIGURE 12.1 Scheme of a motor unit, which is a single α-motorneuron and its asso-
ciated muscle fibers.
many terminal branches, and each axonal branch innervates only one muscle fiber. A single muscle
fiber is innervated by only one motor neuron, but a single motor neuron can innervate more than one
muscle fiber, varying from 9 (e.g., extrinsic eye muscles) to 2000 (e.g., gastrocnemius) muscle fibers
(Feinstein et al., 1955).
The synapse or junction between the axon of a motor neuron and a muscle fiber is known as a
neuromuscular junction, sometimes referred to as a motor end plate (Fig. 12.2). There is a narrow
synaptic cleft between the presynaptic membrane (axon) and the postsynaptic membrane (muscle
fiber membrane). When an action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal, it triggers synaptic
vesicular fusion to the terminal neuron membrane and releases neurotransmitter (acetylcholine) into
FIGURE 12.2 Neuromuscular junction (closer view): (1) presynaptic
terminal; (2) sarcolemma; (3) synaptic vesicles; and (4) acetylcholine
receptors.