Page 229 - Biomimetics : Biologically Inspired Technologies
P. 229
Bar-Cohen : Biomimetics: Biologically Inspired Technologies DK3163_c007 Final Proof page 215 21.9.2005 11:41am
Bio-Nanorobotics 215
Nano man- Power
made devices Source
Micro
Devices
Nano man-
made devices Macro World
Micro
Devices
Nano man-
made devices
Self assembly, sensing, Amplification Macro actuators or
and trigger mechanism mechanisms communication devices
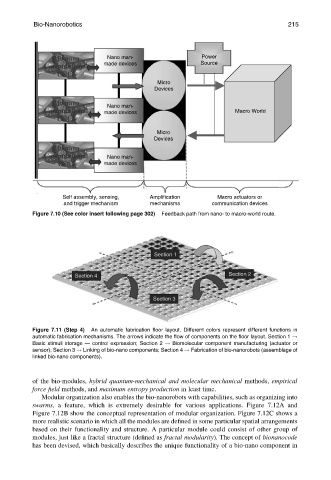
Figure 7.10 (See color insert following page 302) Feedback path from nano- to macro-world route.
Section 1
Section 4 Section 2
Section 3
Figure 7.11 (Step 4) An automatic fabrication floor layout. Different colors represent different functions in
automatic fabrication mechanisms. The arrows indicate the flow of components on the floor layout. Section 1 !
Basic stimuli storage — control expression; Section 2 ! Biomolecular component manufacturing (actuator or
sensor); Section 3 ! Linking of bio-nano components; Section 4 ! Fabrication of bio-nanorobots (assemblage of
linked bio-nano components).
of the bio-modules, hybrid quantum-mechanical and molecular mechanical methods, empirical
force field methods, and maximum entropy production in least time.
Modular organization also enables the bio-nanorobots with capabilities, such as organizing into
swarms, a feature, which is extremely desirable for various applications. Figure 7.12A and
Figure 7.12B show the conceptual representation of modular organization. Figure 7.12C shows a
more realistic scenario in which all the modules are defined in some particular spatial arrangements
based on their functionality and structure. A particular module could consist of other group of
modules, just like a fractal structure (defined as fractal modularity). The concept of bionanocode
has been devised, which basically describes the unique functionality of a bio-nano component in