Page 404 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 404
Extraction, Refining, and Stabilization of Edible Oils 381
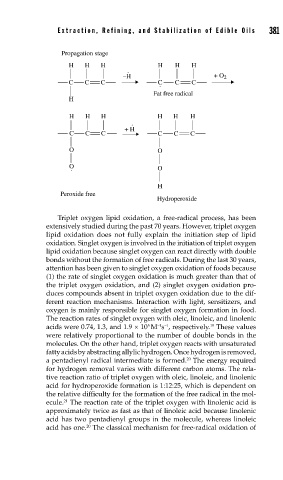
Propagation stage
H H H H H H
.
–H + O 2
C C C C C C
.
Fat free radical
H
H H H H H H
.
+ H
C C C C C C
O O
O
. O
H
Peroxide free
Hydroperoxide
Triplet oxygen lipid oxidation, a free-radical process, has been
extensively studied during the past 70 years. However, triplet oxygen
lipid oxidation does not fully explain the initiation step of lipid
oxidation. Singlet oxygen is involved in the initiation of triplet oxygen
lipid oxidation because singlet oxygen can react directly with double
bonds without the formation of free radicals. During the last 30 years,
attention has been given to singlet oxygen oxidation of foods because
(1) the rate of singlet oxygen oxidation is much greater than that of
the triplet oxygen oxidation, and (2) singlet oxygen oxidation pro-
duces compounds absent in triplet oxygen oxidation due to the dif-
ferent reaction mechanisms. Interaction with light, sensitizers, and
oxygen is mainly responsible for singlet oxygen formation in food.
The reaction rates of singlet oxygen with oleic, linoleic, and linolenic
5
–1 –1
19
acids were 0.74, 1.3, and 1.9 × 10 M s , respectively. These values
were relatively proportional to the number of double bonds in the
molecules. On the other hand, triplet oxygen reacts with unsaturated
fatty acids by abstracting allylic hydrogen. Once hydrogen is removed,
20
a pentadienyl radical intermediate is formed. The energy required
for hydrogen removal varies with different carbon atoms. The rela-
tive reaction ratio of triplet oxygen with oleic, linoleic, and linolenic
acid for hydroperoxide formation is 1:12:25, which is dependent on
the relative difficulty for the formation of the free radical in the mol-
21
ecule. The reaction rate of the triplet oxygen with linolenic acid is
approximately twice as fast as that of linoleic acid because linolenic
acid has two pentadienyl groups in the molecule, whereas linoleic
20
acid has one. The classical mechanism for free-radical oxidation of