Page 146 - Boiler_Operators_Handbook,_Second_Edition
P. 146
Special Systems 131
HTHW plants. I consider them to be far more dangerous
than any other kind of boiler plant. The heated water con-
tains a lot of energy and any rupture of a piping system
or a piece of equipment will result in a steam explosion.
The rupture of an HTHW pipe will discharge almost 100
times as much steam as a steam pipe with steam at the
same temperature. The number and location of exit doors
from a HTHW boiler plant should greatly exceed those
for a steam plant and any control room should have at
least one exit that leads directly outdoors.
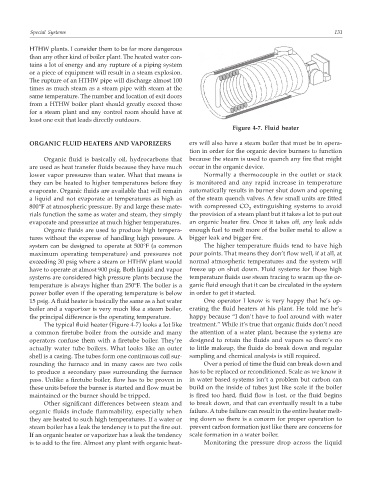
Figure 4-7. Fluid heater
ORGANIC FLUID HEATERS AND VAPORIZERS ers will also have a steam boiler that must be in opera-
tion in order for the organic device burners to function
Organic fluid is basically oil, hydrocarbons that because the steam is used to quench any fire that might
are used as heat transfer fluids because they have much occur in the organic device.
lower vapor pressures than water. What that means is Normally a thermocouple in the outlet or stack
they can be heated to higher temperatures before they is monitored and any rapid increase in temperature
evaporate. Organic fluids are available that will remain automatically results in burner shut down and opening
a liquid and not evaporate at temperatures as high as of the steam quench valves. A few small units are fitted
800°F at atmospheric pressure. By and large these mate- with compressed CO extinguishing systems to avoid
2
rials function the same as water and steam, they simply the provision of a steam plant but it takes a lot to put out
evaporate and pressurize at much higher temperatures. an organic heater fire. Once it takes off, any leak adds
Organic fluids are used to produce high tempera- enough fuel to melt more of the boiler metal to allow a
tures without the expense of handling high pressure. A bigger leak and bigger fire.
system can be designed to operate at 500°F (a common The higher temperature fluids tend to have high
maximum operating temperature) and pressures not pour points. That means they don’t flow well, if at all, at
exceeding 30 psig where a steam or HTHW plant would normal atmospheric temperatures and the system will
have to operate at almost 900 psig. Both liquid and vapor freeze up on shut down. Fluid systems for those high
systems are considered high pressure plants because the temperature fluids use steam tracing to warm up the or-
temperature is always higher than 250°F. The boiler is a ganic fluid enough that it can be circulated in the system
power boiler even if the operating temperature is below in order to get it started.
15 psig. A fluid heater is basically the same as a hot water One operator I know is very happy that he’s op-
boiler and a vaporizer is very much like a steam boiler, erating the fluid heaters at his plant. He told me he’s
the principal difference is the operating temperature. happy because “I don’t have to fool around with water
The typical fluid heater (Figure 4-7) looks a lot like treatment.” While it’s true that organic fluids don’t need
a common firetube boiler from the outside and many the attention of a water plant, because the systems are
operators confuse them with a firetube boiler. They’re designed to retain the fluids and vapors so there’s no
actually water tube boilers. What looks like an outer to little makeup, the fluids do break down and regular
shell is a casing. The tubes form one continuous coil sur- sampling and chemical analysis is still required.
rounding the furnace and in many cases are two coils Over a period of time the fluid can break down and
to produce a secondary pass surrounding the furnace has to be replaced or reconditioned. Scale as we know it
pass. Unlike a firetube boiler, flow has to be proven in in water based systems isn’t a problem but carbon can
these units before the burner is started and flow must be build on the inside of tubes just like scale if the boiler
maintained or the burner should be tripped. is fired too hard, fluid flow is lost, or the fluid begins
Other significant differences between steam and to break down, and that can eventually result in a tube
organic fluids include flammability, especially when failure. A tube failure can result in the entire heater melt-
they are heated to such high temperatures. If a water or ing down so there is a concern for proper operation to
steam boiler has a leak the tendency is to put the fire out. prevent carbon formation just like there are concerns for
If an organic heater or vaporizer has a leak the tendency scale formation in a water boiler.
is to add to the fire. Almost any plant with organic heat- Monitoring the pressure drop across the liquid