Page 253 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 253
238 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
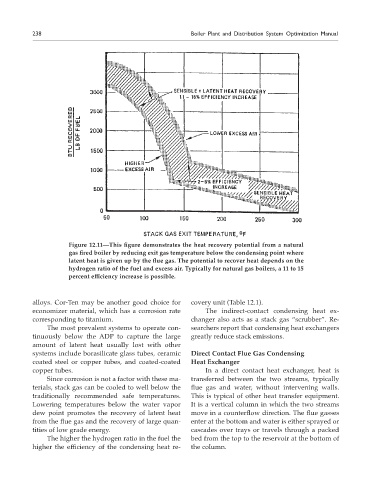
Figure 12.11—This figure demonstrates the heat recovery potential from a natural
gas fired boiler by reducing exit gas temperature below the condensing point where
latent heat is given up by the flue gas. The potential to recover heat depends on the
hydrogen ratio of the fuel and excess air. Typically for natural gas boilers, a 11 to 15
percent efficiency increase is possible.
alloys. Cor-Ten may be another good choice for covery unit (Table 12.1).
economizer material, which has a corrosion rate The indirect-contact condensing heat ex-
corresponding to titanium. changer also acts as a stack gas “scrubber”. Re-
The most prevalent systems to operate con- searchers report that condensing heat exchangers
tinuously below the ADP to capture the large greatly reduce stack emissions.
amount of latent heat usually lost with other
systems include borasilicate glass tubes, ceramic Direct Contact Flue gas Condensing
coated steel or copper tubes, and coated-coated Heat Exchanger
copper tubes. In a direct contact heat exchanger, heat is
Since corrosion is not a factor with these ma- transferred between the two streams, typically
terials, stack gas can be cooled to well below the flue gas and water, without intervening walls.
traditionally recommended safe temperatures. This is typical of other heat transfer equipment.
Lowering temperatures below the water vapor It is a vertical column in which the two streams
dew point promotes the recovery of latent heat move in a counterflow direction. The flue gasses
from the flue gas and the recovery of large quan- enter at the bottom and water is either sprayed or
tities of low grade energy. cascades over trays or travels through a packed
The higher the hydrogen ratio in the fuel the bed from the top to the reservoir at the bottom of
higher the efficiency of the condensing heat re- the column.