Page 191 - Bridge and Highway Structure Rehabilitation and Repair
P. 191
166 SECTION 2 STRENGTHENING AND REPAIR WORK
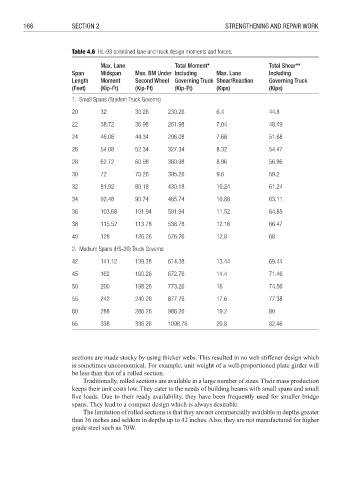
Table 4.6 HL-93 combined lane and truck design moments and forces.
Max. Lane Total Moment* Total Shear**
Span Midspan Max. BM Under Including Max. Lane Including
Length Moment Second Wheel Governing Truck Shear/Reaction Governing Truck
(Feet) (Kip-Ft) (Kip-Ft) (Kip-Ft) (Kips) (Kips)
1. Small Spans (Tandem Truck Governs)
20 32 30.26 230.26 6.4 44.8
22 38.72 36.98 261.98 7.04 48.49
24 46.08 44.34 296.08 7.68 51.68
26 54.08 52.34 327.34 8.32 54.47
28 62.72 60.98 360.98 8.96 56.96
30 72 70.26 395.26 9.6 59.2
32 81.92 80.18 430.18 10.24 61.24
34 92.48 90.74 465.74 10.88 63.11
36 103.68 101.94 501.94 11.52 64.85
38 115.52 113.78 538.78 12.16 66.47
40 128 126.26 576.26 12.8 68
2. Medium Spans (HS-20) Truck Governs
42 141.12 139.38 614.38 13.44 69.44
45 162 160.26 672.76 14.4 71.46
50 200 198.26 773.26 16 74.56
55 242 240.26 877.76 17.6 77.38
60 288 286.26 986.26 19.2 80
65 338 336.26 1098.76 20.8 82.46
sections are made stocky by using thicker webs. This resulted in no web stiffener design which
is sometimes uneconomical. For example, unit weight of a well-proportioned plate girder will
be less than that of a rolled section.
Traditionally, rolled sections are available in a large number of sizes. Their mass production
keeps their unit costs low. They cater to the needs of building beams with small spans and small
live loads. Due to their ready availability, they have been frequently used for smaller bridge
spans. They lead to a compact design which is always desirable.
The limitation of rolled sections is that they are not commercially available in depths greater
than 36 inches and seldom in depths up to 42 inches. Also, they are not manufactured for higher
grade steel such as 70W.