Page 200 - Bridge and Highway Structure Rehabilitation and Repair
P. 200
CHAPTER 4 AN ANALYTICAL APPROACH TO FRACTURE AND FAILURE 175
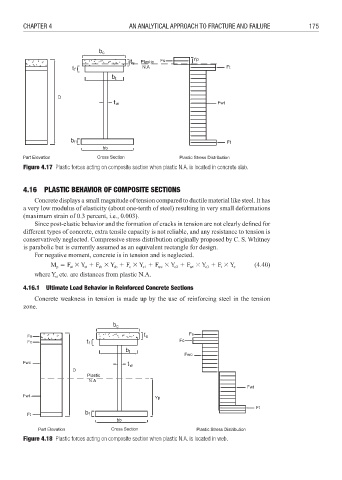
Figure 4.17 Plastic forces acting on composite section when plastic N.A. is located in concrete slab.
4.16 PLASTIC BEHAVIOR OF COMPOSITE SECTIONS
Concrete displays a small magnitude of tension compared to ductile material like steel. It has
a very low modulus of elasticity (about one-tenth of steel) resulting in very small deformations
(maximum strain of 0.3 percent, i.e., 0.003).
Since post-elastic behavior and the formation of cracks in tension are not clearly defi ned for
different types of concrete, extra tensile capacity is not reliable, and any resistance to tension is
conservatively neglected. Compressive stress distribution originally proposed by C. S. Whitney
is parabolic but is currently assumed as an equivalent rectangle for design.
For negative moment, concrete is in tension and is neglected.
M 3 F 8 Y 4 F 8 Y 4 F 8 Y 4 F 8 Y 4 F 8 Y 4 F 8 Y c (4.40)
st
p
st
c
sb
sb
t
c3
wt
c1
wc
c2
where Y etc. are distances from plastic N.A.
st
4.16.1 Ultimate Load Behavior in Reinforced Concrete Sections
Concrete weakness in tension is made up by the use of reinforcing steel in the tension
zone.
Figure 4.18 Plastic forces acting on composite section when plastic N.A. is located in web.