Page 142 - Build Your Own Transistor Radios a Hobbyists Guide to High-Performance and Low-Powered Radio Circuits
P. 142
+ 1.5
,01 uf
VC1RF VCl RF Pad
Ra
270 pr 20 pr C13
lOOK
C7 + 1 ,5 Q4 .0022 uf
T2
• L l' Primary MPSH10 (I')
4
330 Uh
r---..---(2IiC 2
C14 1.1 M
1 ut
+ 1.5
R13
lOOK
VC l Osc VCl Osc Pad T1
+ 1,5
20 pr
33~ R4 R10
C16
330 pt R3 56K lOOK
e10
-Pri 56K ~
01 .01 ut
rh Cl lN9l4
Note # 2: Use Low SI de Tap for T2. T3 & T 4
,01 uf 02
lN914
Note # 1: For 421Fl 01 ,Tl
Vel_Osc Pad 0 Low Side
Tap ofT 1 ,
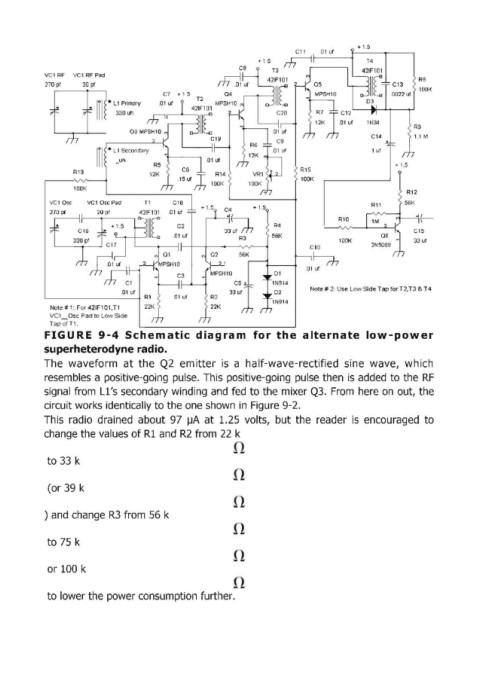
FIGURE 9-4 Schematic diagram for the alternate low-power
superheterodyne radio.
The waveform at the Q2 emitter is a half-wave-rectified sine wave, which
resembles a positive-going pulse. This positive-going pulse then is added to the RF
signal from Ll's secondary winding and fed to the mixer Q3. From here on out, the
circuit works identically to the one shown in Figure 9-2.
This radio drained about 97 ~A at 1.25 volts, but the reader is encouraged to
change the values of RI and R2 from 22 k
to 33 k
(or 39 k
) and change R3 from 56 k
to 75 k
or 100 k
to lower the power consumption further.