Page 47 - Buried Pipe Design
P. 47
External Loads 25
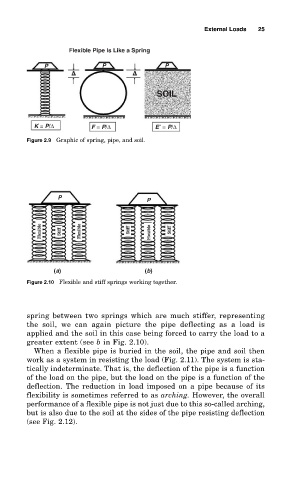
Flexible Pipe Is Like a Spring
P P P
Δ Δ
SOIL
K = P/Δ F = P/Δ E′ = P/Δ
Figure 2.9 Graphic of spring, pipe, and soil.
P
P
(a) (b)
Figure 2.10 Flexible and stiff springs working together.
spring between two springs which are much stiffer, representing
the soil, we can again picture the pipe deflecting as a load is
applied and the soil in this case being forced to carry the load to a
greater extent (see b in Fig. 2.10).
When a flexible pipe is buried in the soil, the pipe and soil then
work as a system in resisting the load (Fig. 2.11). The system is sta-
tically indeterminate. That is, the deflection of the pipe is a function
of the load on the pipe, but the load on the pipe is a function of the
deflection. The reduction in load imposed on a pipe because of its
flexibility is sometimes referred to as arching. However, the overall
performance of a flexible pipe is not just due to this so-called arching,
but is also due to the soil at the sides of the pipe resisting deflection
(see Fig. 2.12).