Page 116 -
P. 116
OPEN BUSINESS MODELS 2WKHU À UP V
..K <93[(6
F$3=HC\
PATTERNS <93[(6
7%6(3%9'
D(5?%4'4,X F$3=:)>>CHD
D(5?%4'4,X
D(5?%4'4,X
#9;( <93[(6
#9;(
CZ6(3%9'
D(5?%4'4,X
D(5?%4'4,X
D(5?%4'4,X
#9;(
#9;(
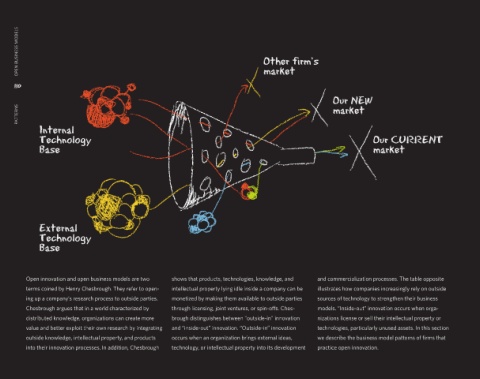
Open innovation and open business models are two shows that products, technologies, knowledge, and and commercialization processes. The table opposite
terms coined by Henry Chesbrough. They refer to open- intellectual property lying idle inside a company can be illustrates how companies increasingly rely on outside
ing up a company’s research process to outside parties. monetized by making them available to outside parties sources of technology to strengthen their business
Chesbrough argues that in a world characterized by through licensing, joint ventures, or spin-oΩs. Ches- models. “Inside-out” innovation occurs when orga-
distributed knowledge, organizations can create more brough distinguishes between "outside-in" innovation nizations license or sell their intellectual property or
value and better exploit their own research by integrating and “inside-out” innovation. “Outside-in” innovation technologies, particularly unused assets. In this section
outside knowledge, intellectual property, and products occurs when an organization brings external ideas, we describe the business model patterns of fi rms that
into their innovation processes. In addition, Chesbrough technology, or intellectual property into its development practice open innovation.
!"#$%&'(%)*+(%,,---113 /012013---245:-67