Page 467 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 467
THB14 9/19/03 7:58 PM Page 455
SPECIAL CAM MECHANISMS 455
The relative tangential velocity between two bodies with P and Q, the points in contact,
is
V = V - V (14.1)
PQ P A Q A
where V P/A = velocity of contact point P on body B with respect to the ground A
V Q/A = velocity of contact point Q on body B with respect to the ground A
Thus, given the velocity of one body at any instant, we can find the velocity
of the contacting body and the relative sliding velocity given the cam-follower
characteristics.
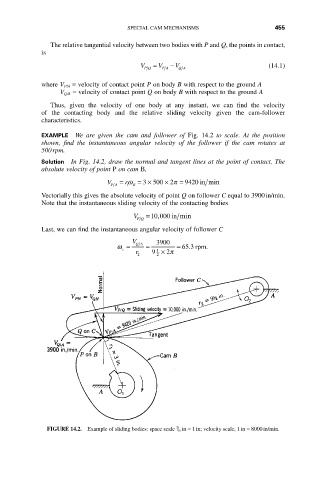
EXAMPLE We are given the cam and follower of Fig. 14.2 to scale. At the position
shown, find the instantaneous angular velocity of the follower if the cam rotates at
500rpm.
Solution In Fig. 14.2, draw the normal and tangent lines at the point of contact. The
absolute velocity of point P on cam B,
3
V PA = rw B = ¥ 500 ¥ p = 9420 in min
2
i
Vectorially this gives the absolute velocity of point Q on follower C equal to 3900in/min.
Note that the instantaneous sliding velocity of the contacting bodies
V PQ =10 000 in min
,
Last, we can find the instantaneous angular velocity of follower C
V QA 3900
w = = = 65 3. rpm.
c 1
r 2 9 2 ¥ 2 p
5
FIGURE 14.2. Example of sliding bodies: space scale / 16 in = 1in; velocity scale, 1in = 8000in/min.