Page 227 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 227
218 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
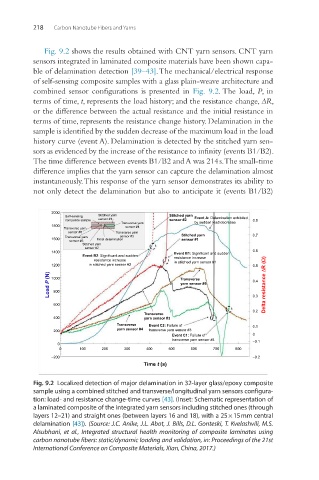
Fig. 9.2 shows the results obtained with CNT yarn sensors. CNT yarn
sensors integrated in laminated composite materials have been shown capa-
ble of delamination detection [39–43]. The mechanical/electrical response
of self-sensing composite samples with a glass plain-weave architecture and
combined sensor configurations is presented in Fig. 9.2. The load, P, in
terms of time, t, represents the load history; and the resistance change, ∆R,
or the difference between the actual resistance and the initial resistance in
terms of time, represents the resistance change history. Delamination in the
sample is identified by the sudden decrease of the maximum load in the load
history curve (event A). Delamination is detected by the stitched yarn sen-
sors as evidenced by the increase of the resistance to infinity (events B1/B2).
The time difference between events B1/B2 and A was 214 s. The small-time
difference implies that the yarn sensor can capture the delamination almost
instantaneously. This response of the yarn sensor demonstrates its ability to
not only detect the delamination but also to anticipate it (events B1/B2)
2000
Self-sensing Stitched yarn Stitched yarn Event A: Delamination exhibited
composite sample sensor #1 Transverse yarn sensor #2 by sudden load decrease 0.8
1800 sensor #4
Transverse yarn
sensor #6 Transverse yarn
Transverse yarn sensor #3 Stitched yarn 0.7
1600 Initial delamination sensor #1
sensor #5
Stitched yarn
sensor #2
1400 Event B1: Significant and sudden 0.6
Event B2: Significant and sudden resistance increase
resistance increase in stitched yarn sensor #1
1200 in stitched yarn sensor #2 0.5
Load P (N) 1000 Transverse 0.4 Delta resistance DR (W)
yarn sensor #5
800
600 0.3
0.2
Transverse
400 yarn sensor #3
Transverse Event C2: Failure of 0.1
yarn sensor #4 transverse yarn sensor #3
200
Event C1: Failure of 0
transverse yarn sensor #4 –0.1
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
–200 –0.2
Time t (s)
Fig. 9.2 Localized detection of major delamination in 32-layer glass/epoxy composite
sample using a combined stitched and transverse/longitudinal yarn sensors configura-
tion: load- and resistance change-time curves [43]. (Inset: Schematic representation of
a laminated composite of the integrated yarn sensors including stitched ones (through
layers 12–21) and straight ones (between layers 16 and 18), with a 25 × 15 mm central
delamination [43]). (Source: J.C. Anike, J.L. Abot, J. Bills, D.L. Gonteski, T. Kvelashvili, M.S.
Alsubhani, et al., Integrated structural health monitoring of composite laminates using
carbon nanotube fibers: static/dynamic loading and validation, in: Proceedings of the 21st
International Conference on Composite Materials, Xian, China, 2017.)