Page 232 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 232
Sensors based on CNT yarns 223
400
3 2 CNT fiber prestrain
No
Relative change in resistance 350 1 0 0 100 200 300 100 %
only
300
250
200
prestrain
400
150
100
50
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
(A) 8000 Strain (%)
Relative change in resistance (%) 6000
4000
2000
0
0 5 10 15
Strain (%)
(B)
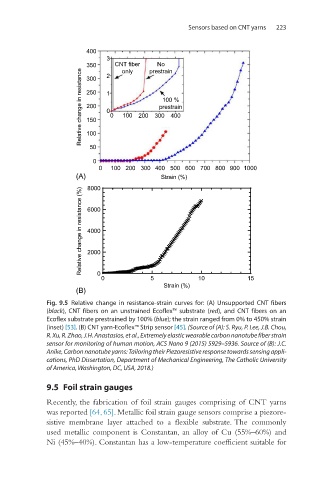
Fig. 9.5 Relative change in resistance-strain curves for: (A) Unsupported CNT fibers
(black), CNT fibers on an unstrained Ecoflex™ substrate (red), and CNT fibers on an
Ecoflex substrate prestrained by 100% (blue); the strain ranged from 0% to 450% strain
(inset) [53]. (B) CNT yarn-Ecoflex™ Strip sensor [45]. (Source of (A): S. Ryu, P. Lee, J.B. Chou,
R. Xu, R. Zhao, J.H. Anastasios, et al., Extremely elastic wearable carbon nanotube fiber strain
sensor for monitoring of human motion, ACS Nano 9 (2015) 5929–5936. Source of (B): J.C.
Anike, Carbon nanotube yarns: Tailoring their Piezoresistive response towards sensing appli-
cations, PhD Dissertation, Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Catholic University
of America, Washington, DC, USA, 2018.)
9.5 Foil strain gauges
Recently, the fabrication of foil strain gauges comprising of CNT yarns
was reported [64, 65]. Metallic foil strain gauge sensors comprise a piezore-
sistive membrane layer attached to a flexible substrate. The commonly
used metallic component is Constantan, an alloy of Cu (55%–60%) and
Ni (45%–40%). Constantan has a low-temperature coefficient suitable for