Page 233 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 233
224 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
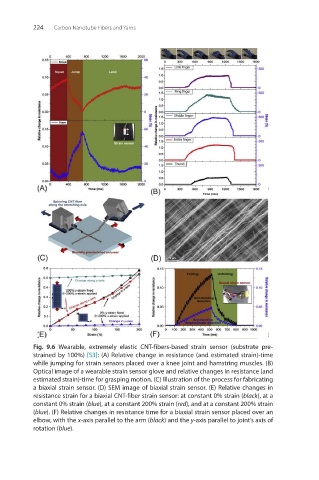
Fig. 9.6 Wearable, extremely elastic CNT-fibers-based strain sensor (substrate pre-
strained by 100%) [53]: (A) Relative change in resistance (and estimated strain)-time
while jumping for strain sensors placed over a knee joint and hamstring muscles. (B)
Optical image of a wearable strain sensor glove and relative changes in resistance (and
estimated strain)-time for grasping motion. (C) Illustration of the process for fabricating
a biaxial strain sensor. (D) SEM image of biaxial strain sensor. (E) Relative changes in
resistance strain for a biaxial CNT-fiber strain sensor: at constant 0% strain (black), at a
constant 0% strain (blue), at a constant 200% strain (red), and at a constant 200% strain
(blue). (F) Relative changes in resistance time for a biaxial strain sensor placed over an
elbow, with the x-axis parallel to the arm (black) and the y-axis parallel to joint’s axis of
rotation (blue).