Page 239 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 239
Sensors based on CNT yarns 229
0.045 1.33
Strain Resistance
0.04
1.13
0.035
0.93
0.03
e (%) 0.025 0.73 ∆R/R 0 (%)
0.02
0.53
0.015
0.33
0.01
0.13
0.005
0 −0.07
0 200 400 600
(A) t (s)
1.2
1
0.8 GF=35.395
2
R =0.9994
∆R/R 0 (%) 0.6 Loading
Linear (loading)
0.4
0.2
0
0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05
−0.2
(B) e (%)
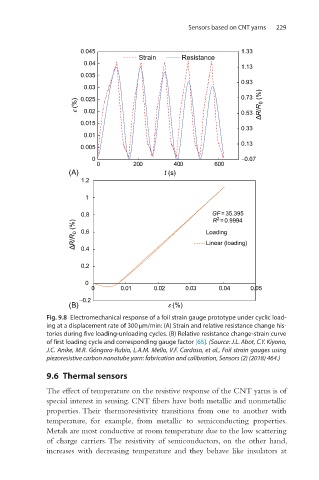
Fig. 9.8 Electromechanical response of a foil strain gauge prototype under cyclic load-
ing at a displacement rate of 300 μm/min: (A) Strain and relative resistance change his-
tories during five loading-unloading cycles. (B) Relative resistance change-strain curve
of first loading cycle and corresponding gauge factor [65]. (Source: J.L. Abot, C.Y. Kiyono,
J.C. Anike, M.R. Góngora-Rubio, L.A.M. Mello, V.F. Cardoso, et al., Foil strain gauges using
piezoresistive carbon nanotube yarn: fabrication and calibration, Sensors (2) (2018) 464.)
9.6 Thermal sensors
The effect of temperature on the resistive response of the CNT yarns is of
special interest in sensing. CNT fibers have both metallic and nonmetallic
properties. Their thermoresistivity transitions from one to another with
temperature, for example, from metallic to semiconducting properties.
Metals are most conductive at room temperature due to the low scattering
of charge carriers. The resistivity of semiconductors, on the other hand,
increases with decreasing temperature and they behave like insulators at