Page 243 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 243
Sensors based on CNT yarns 233
shown in Fig. 9.10 shows a negative thermoresistive coefficient, that is,
R decreases with increasing temperature like earlier reports. However, the
transition behavior was not seen in the R-T curve even up to 300 K as seen
in Fig. 9.10C. This indicates that some molecular rearrangement and pos-
sibly tunneling could be happening during the heating and cooling cycles
that affect the thermoresistivity. Further studies are needed to fully explain
this behavior.
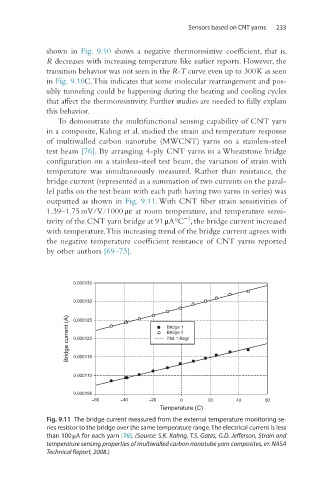
To demonstrate the multifunctional sensing capability of CNT yarn
in a composite, Kahng et al. studied the strain and temperature response
of multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) yarns on a stainless-steel
test beam [76]. By arranging 4-ply CNT yarns in a Wheatstone bridge
configuration on a stainless-steel test beam, the variation of strain with
temperature was simultaneously measured. Rather than resistance, the
bridge current (represented as a summation of two currents on the paral-
lel paths on the test beam with each path having two yarns in series) was
outputted as shown in Fig. 9.11. With CNT fiber strain sensitivities of
1.39–1.75 mV/V/1000 με at room temperature, and temperature sensi-
−1
tivity of the CNT yarn bridge at 91 μA°C , the bridge current increased
with temperature. This increasing trend of the bridge current agrees with
the negative temperature coefficient resistance of CNT yarns reported
by other authors [69–73].
0.000135
0.000130
Bridge current (A) 0.000120 Bridge 1
0.000125
Bridge 2
Plot 1 Regr
0.000115
0.000110
0.000105
−60 −40 −20 0 20 40 60
Temperature (C)
Fig. 9.11 The bridge current measured from the external temperature monitoring se-
ries resistor to the bridge over the same temperature range. The electrical current is less
than 100 μA for each yarn [76]. (Source: S.K. Kahng, T.S. Gates, G.D. Jefferson, Strain and
temperature sensing properties of multiwalled carbon nanotube yarn composites, in: NASA
Technical Report, 2008.)