Page 27 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 27
20 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
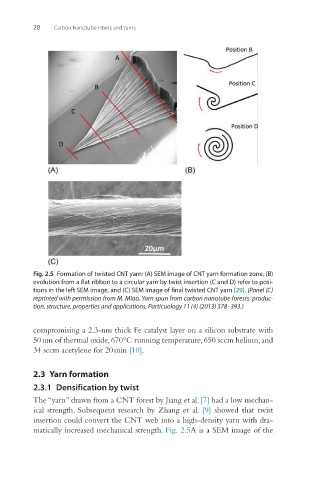
Fig. 2.5 Formation of twisted CNT yarn: (A) SEM image of CNT yarn formation zone, (B)
evolution from a flat ribbon to a circular yarn by twist insertion (C and D) refer to posi-
tions in the left SEM image, and (C) SEM image of final twisted CNT yarn [29]. (Panel (C)
reprinted with permission from M. Miao, Yarn spun from carbon nanotube forests: produc-
tion, structure, properties and applications, Particuology 11 (4) (2013) 378–393.)
compromising a 2.3-nm thick Fe catalyst layer on a silicon substrate with
50 nm of thermal oxide, 670°C running temperature, 650 sccm helium, and
34 sccm acetylene for 20 min [10].
2.3 Yarn formation
2.3.1 Densification by twist
The “yarn” drawn from a CNT forest by Jiang et al. [7] had a low mechan-
ical strength. Subsequent research by Zhang et al. [9] showed that twist
insertion could convert the CNT web into a high-density yarn with dra-
matically increased mechanical strength. Fig. 2.5A is a SEM image of the