Page 29 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 29
22 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
CNT forest
Motor Motor
CNT fiber
CNT shcct
Twist
(A) Substrate Draw
(C) (B)
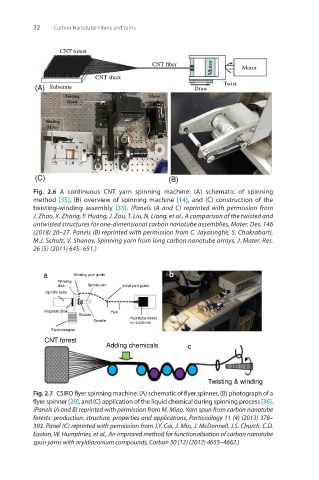
Fig. 2.6 A continuous CNT yarn spinning machine: (A) schematic of spinning
method [35], (B) overview of spinning machine [14], and (C) construction of the
twisting-winding assembly [35]. (Panels (A and C) reprinted with permission from
J. Zhao, X. Zhang, Y. Huang, J. Zou, T. Liu, N. Liang, et al., A comparison of the twisted and
untwisted structures for one-dimensional carbon nanotube assemblies, Mater. Des. 146
(2018) 20–27. Panels (B) reprinted with permission from C. Jayasinghe, S. Chakrabarti,
M.J. Schulz, V. Shanov, Spinning yarn from long carbon nanotube arrays, J. Mater. Res.
26 (5) (2011) 645–651.)
a Winding yarn guide
Winding
disk Spindle pin Initial yarn guide
Spindle base
Magnetic Disk Yarn
Bobbin Nanotube forest
Spindle on substrate
Electromagnet
CNT forest
Adding chemicals c
Twisting & winding
Fig. 2.7 CSIRO flyer spinning machine: (A) schematic of flyer spinner, (B) photograph of a
flyer spinner [29], and (C) application of the liquid chemical during spinning process [36].
(Panels (A and B) reprinted with permission from M. Miao, Yarn spun from carbon nanotube
forests: production, structure, properties and applications, Particuology 11 (4) (2013) 378–
393. Panel (C) reprinted with permission from J.Y. Cai, J. Min, J. McDonnell, J.S. Church, C.D.
Easton, W. Humphries, et al., An improved method for functionalisation of carbon nanotube
spun yarns with aryldiazonium compounds, Carbon 50 (12) (2012) 4655–4662.)