Page 14 - Carbonate Sedimentology and Sequence Stratigraphy
P. 14
CHAPTER 1: ESSENTIALS OF NEIGHBORING DISCIPLINES 5
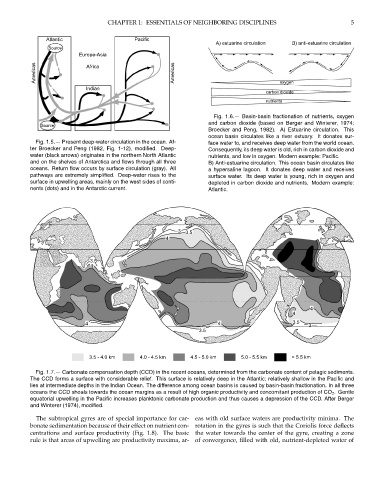
Atlantic Pacific
A) estuarine circulation B) anti-estuarine circulation
Source
Europe-Asia
Americas Africa Americas
Indian oxygen
carbon dioxide
nutrients
Fig. 1.6.— Basin-basin fractionation of nutrients, oxygen
and carbon dioxide (based on Berger and Winterer, 1974;
Source
Broecker and Peng, 1982). A) Estuarine circulation. This
ocean basin circulates like a river estuary. It donates sur-
Fig. 1.5.— Present deep-water circulation in the ocean. Af- face water to, and receives deep water from the world ocean.
ter Broecker and Peng (1982, Fig. 1-12), modified. Deep- Consequently, its deep water is old, rich in carbon dioxide and
water (black arrows) originates in the northern North Atlantic nutrients, and low in oxygen. Modern example: Pacific.
and on the shelves of Antarctica and flows through all three B) Anti-estuarine circulation. This ocean basin circulates like
oceans. Return flow occurs by surface circulation (gray). All a hypersaline lagoon. It donates deep water and receives
pathways are extremely simplified. Deep-water rises to the surface water. Its deep water is young, rich in oxygen and
surface in upwelling areas, mainly on the west sides of conti- depleted in carbon dioxide and nutrients. Modern example:
nents (dots) and in the Antarctic current. Atlantic.
3 3.5
4
3.5
4
4
4
4 4 3.5 3
3.5
3.5 - 4.0 km 4.0 - 4.5 km 4.5 - 5.0 km 5.0 - 5.5 km > 5.5 km
Fig. 1.7.— Carbonate compensation depth (CCD) in the recent oceans, determined from the carbonate content of pelagic sediments.
The CCD forms a surface with considerable relief. This surface is relatively deep in the Atlantic; relatively shallow in the Pacific and
lies at intermediate depths in the Indian Ocean. The difference among ocean basins is caused by basin-basin fractionation. In all three
oceans the CCD shoals towards the ocean margins as a result of high organic productivity and concomitant production of CO 2 . Gentle
equatorial upwelling in the Pacific increases planktonic carbonate production and thus causes a depression of the CCD. After Berger
and Winterer (1974), modified.
The subtropical gyres are of special importance for car- eas with old surface waters are productivity minima. The
bonate sedimentation because of their effect on nutrient con- rotation in the gyres is such that the Coriolis force deflects
centrations and surface productivity (Fig. 1.8). The basic the water towards the center of the gyre, creating a zone
rule is that areas of upwelling are productivity maxima, ar- of convergence, filled with old, nutrient-depleted water of