Page 156 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 156
Polycondensation Polymers 119
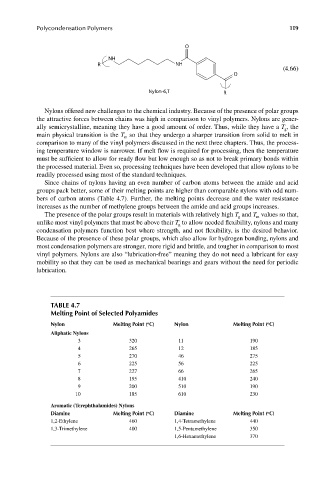
O
NH
R NH
(4.66)
O
Nylon-6,T R
Nylons offered new challenges to the chemical industry. Because of the presence of polar groups
the attractive forces between chains was high in comparison to vinyl polymers. Nylons are gener-
ally semicrystalline, meaning they have a good amount of order. Thus, while they have a T , the
g
main physical transition is the T so that they undergo a sharper transition from solid to melt in
m
comparison to many of the vinyl polymers discussed in the next three chapters. Thus, the process-
ing temperature window is narrower. If melt flow is required for processing, then the temperature
must be suffi cient to allow for ready fl ow but low enough so as not to break primary bonds within
the processed material. Even so, processing techniques have been developed that allow nylons to be
readily processed using most of the standard techniques.
Since chains of nylons having an even number of carbon atoms between the amide and acid
groups pack better, some of their melting points are higher than comparable nylons with odd num-
bers of carbon atoms (Table 4.7). Further, the melting points decrease and the water resistance
increases as the number of methylene groups between the amide and acid groups increases.
The presence of the polar groups result in materials with relatively high T and T values so that,
m
g
unlike most vinyl polymers that must be above their T to allow needed flexibility, nylons and many
g
condensation polymers function best where strength, and not flexibility, is the desired behavior.
Because of the presence of these polar groups, which also allow for hydrogen bonding, nylons and
most condensation polymers are stronger, more rigid and brittle, and tougher in comparison to most
vinyl polymers. Nylons are also “lubrication-free” meaning they do not need a lubricant for easy
mobility so that they can be used as mechanical bearings and gears without the need for periodic
lubrication.
TABLE 4.7
Melting Point of Selected Polyamides
Nylon Melting Point ( C) Nylon Melting Point ( C)
o
o
Aliphatic Nylons
3 320 11 190
4 265 12 185
5 270 46 275
6 225 56 225
7 227 66 265
8 195 410 240
9 200 510 190
10 185 610 230
Aromatic (Terephthalamides) Nylons
o
o
Diamine Melting Point ( C) Diamine Melting Point ( C)
1,2-Ethylene 460 1,4-Tetramethylene 440
1,3-Trimethylene 400 1,5-Pentamethylene 350
1,6-Hexamethylene 370
9/14/2010 3:38:24 PM
K10478.indb 119 9/14/2010 3:38:24 PM
K10478.indb 119