Page 199 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 199
162 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
using mixtures of triethylaluminum and titanium tetrachloride. Another Nobel Laureate, Giulio
Natta, used Ziegler’s complex coordination catalyst to produce crystalline, stereoregular polypro-
pylene (PP). These catalysts are now known as Ziegler-Natta (or Natta-Ziegler) catalysts.
In general, a Ziegler-Natta catalyst is a combination of a transition-metal compound from Groups
IVB (4) to VIIIB (10) and an organometallic compound of a metal from Groups IA (1) to IIIA
(13) in the periodic table. It is customary to refer to the transition-metal compounds as the catalyst
(because reaction occurs at the transition-metal atom site) and the organometallic compound as the
cocatalyst.
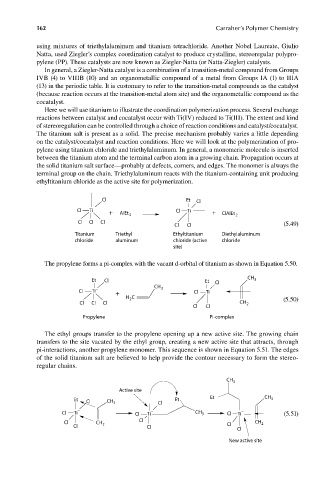
Here we will use titanium to illustrate the coordination polymerization process. Several exchange
reactions between catalyst and cocatalyst occur with Ti(IV) reduced to Ti(III). The extent and kind
of stereoregulation can be controlled through a choice of reaction conditions and catalyst/cocatalyst.
The titanium salt is present as a solid. The precise mechanism probably varies a little depending
on the catalyst/cocatalyst and reaction conditions. Here we will look at the polymerization of pro-
pylene using titanium chloride and triethylaluminum. In general, a monomeric molecule is inserted
between the titanium atom and the terminal carbon atom in a growing chain. Propagation occurs at
the solid titanium salt surface—probably at defects, corners, and edges. The monomer is always the
terminal group on the chain. Triethylaluminum reacts with the titanium-containing unit producing
ethyltitanium chloride as the active site for polymerization.
Cl Et Cl
−
Cl Ti Cl Ti
+ AlEt 3 + ClAlEt 2
Cl Cl Cl
Cl Cl (5.49)
Titanium Triethyl Ethyltitanium Diethylaluminum
chloride aluminum chloride (active chloride
site)
The propylene forms a pi-complex with the vacant d-orbital of titanium as shown in Equation 5.50.
CH
Et Cl Et Cl 3
CH 3
Cl Ti – Cl Ti
+
H C (5.50)
2
Cl Cl Cl CH 2
Cl Cl
Propylene Pi-complex
The ethyl groups transfer to the propylene opening up a new active site. The growing chain
transfers to the site vacated by the ethyl group, creating a new active site that attracts, through
pi-interactions, another propylene monomer. This sequence is shown in Equation 5.51. The edges
of the solid titanium salt are believed to help provide the contour necessary to form the stereo-
regular chains.
CH 3
Active site
Et CH
Et Cl CH 3 Cl Et 3
− − −
Cl Ti Cl Ti CH 3 Cl Ti (5.51)
Cl CH Cl CH 2
Cl 2 Cl Cl Cl
New active site
9/14/2010 3:39:01 PM
K10478.indb 162 9/14/2010 3:39:01 PM
K10478.indb 162