Page 158 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 158
asymmetric reduction using nonmetallic catalysts 145
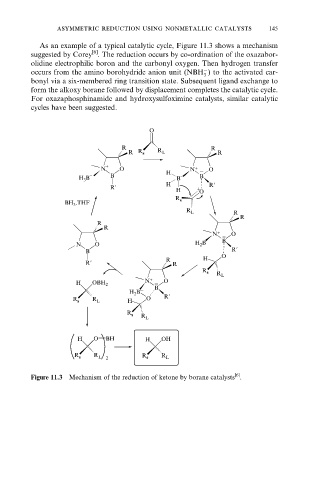
As an example of a typical catalytic cycle, Figure 11.3 shows a mechanism
[6]
suggested by Corey . The reduction occurs by co-ordination of the oxazabor-
olidine electrophilic boron and the carbonyl oxygen. Then hydrogen transfer
occurs from the amino borohydride anion unit (NBH ) to the activated car-
ÿ
3
bonyl via a six-membered ring transition state. Subsequent ligand exchange to
form the alkoxy borane followed by displacement completes the catalytic cycle.
For oxazaphosphinamide and hydroxysulfoximine catalysts, similar catalytic
cycles have been suggested.
O
R R
R R s R L R
N + O N + − O
− B H
H B B − B
3
H R9
R9 +
H O
R s
BH 3 .THF
R
R L
R
R
R
N + − O
N O H 2 B B
B R9
O
R H
R9 R
R s
R L
H OBH 2 N + − O
H 2 B − B
O R9
H
R s R L
R s
R L
H O BH H OH
R s R L R s R L
2
[6]
Figure 11.3 Mechanism of the reduction of ketone by borane catalysts .