Page 157 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 157
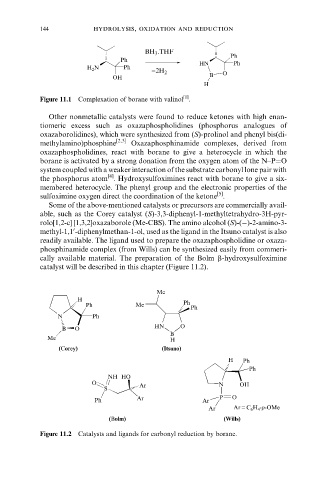
144 hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction
BH 3 .THF
Ph
Ph
HN Ph
H 2 N Ph
−2H 2 O
OH B
H
[1]
Figure 11.1 Complexation of borane with valinol .
Other nonmetallic catalysts were found to reduce ketones with high enan-
tiomeric excess such as oxazaphospholidines (phosphorus analogues of
oxazaborolidines), which were synthesized from (S)-prolinol and phenyl bis(di-
methylamino)phosphine [2,3] Oxazaphosphinamide complexes, derived from
oxazaphospholidines, react with borane to give a heterocycle in which the
borane is activated by a strong donation from the oxygen atom of the N±PO
system coupled with a weaker interaction of the substrate carbonyl lone pair with
[4]
the phosphorus atom . Hydroxysulfoximines react with borane to give a six-
membered heterocycle. The phenyl group and the electronic properties of the
[5]
sulfoximine oxygen direct the coordination of the ketone .
Some of the above-mentioned catalysts or precursors are commercially avail-
able, such as the Corey catalyst (S)-3,3-diphenyl-1-methyltetrahydro-3H-pyr-
rolo[1,2-c] [1,3,2]oxazaborole (Me-CBS). The amino alcohol (S)-(ÿ)-2-amino-3-
methyl-1,1 -diphenylmethan-1-ol, used as the ligand in the Itsuno catalyst is also
0
readily available. The ligand used to prepare the oxazaphospholidine or oxaza-
phosphinamide complex (from Wills) can be synthesized easily from commeri-
cally available material. The preparation of the Bolm b-hydroxysulfoximine
catalyst will be described in this chapter (Figure 11.2).
Me
H
Ph Me Ph
Ph
N Ph
B O HN O
B
Me H
(Corey) (Itsuno)
H Ph
Ph
NH HO
O Ar N OH
S
Ph Ar Ar P O
Ar Ar = C 6 H 4 -p-OMe
(Bolm) (Wills)
Figure 11.2 Catalysts and ligands for carbonyl reduction by borane.