Page 94 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 94
80 hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction
(2R, 3R)-enantiomer: R t 52.6 min. The ee can be determined by analysis of
19
the ester derived from ()-MTPA chloride ( F NMR (250 MHz, CDCl 3 ):
d ÿ 70:8 (s, (2R,3R)-enantiomer); ÿ72.0 (s, (2S,3S)-enantiomer)).
1
H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl 3 ): d 3.91 (d, J 13.5 Hz, 1H); 3.60 (dd, J
13.4 Hz, J 4.1 Hz, 1H); 2.94 (m, 2H); 2.53 (m, 1H); 1.53 (m, 4H); 0.96 (t, J
7.1 Hz, 3H, CH 3 ).
ÿ1
IR (CHCl 3 , cm : 3589 (C±O), 3009, 2965, 2937, 2877 (C±H), 1458 (C±H,
CH 3 ), 1382, 1203 (C±OH, C±O±C), 1095, 1030, 970, 924, 897, 848.
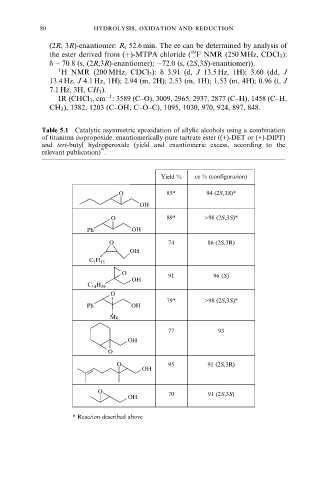
Table 5.1 Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of allylic alcohols using a combination
of titanium isopropoxide. enantiomerically pure tartrate ester ((+)-DET or (+)-DIPT)
and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (yield and enantiomeric excess, according to the
[4]
relevant publication) .
Yield % ee % (configuration)
O 85* 94 (2S,3S)*
OH
O 89* >98 (2S,3S)*
Ph OH
O 74 86 (2S,3R)
OH
C 7 H 15
O 91 96 (S)
OH
C 14 H 29
O
79* >98 (2S,3S)*
Ph OH
Me
77 93
OH
O
O 95 91 (2S,3R)
OH
O 70 91 (2S,3S)
OH
* Reaction described above