Page 47 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 47
Chalcogenide Glasses 25
very specific bonding angle requirements to nearest neighbors which
resist being changed by force.
Myuller points out that the deformation of covalently bonded
28
substances in the liquid state during viscous flow requires much
more energy than the deformation of materials bonded ionically.
Thus, covalent melts are viscous. The bonding requirements for ionic
and metallic substances are not rigid with respect to bonding angles.
Thus, metallic and ionic melts are not viscous and freeze into a solid
when cooled to their melting points.
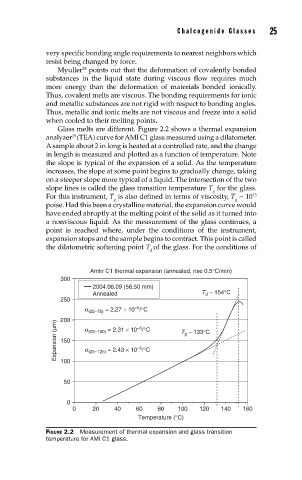
Glass melts are different. Figure 2.2 shows a thermal expansion
29
analyzer (TEA) curve for AMI C1 glass measured using a dilatometer.
A sample about 2 in long is heated at a controlled rate, and the change
in length is measured and plotted as a function of temperature. Note
the slope is typical of the expansion of a solid. As the temperature
increases, the slope at some point begins to gradually change, taking
on a steeper slope more typical of a liquid. The intersection of the two
slope lines is called the glass transition temperature T for the glass.
g
For this instrument, T is also defined in terms of viscosity, T ~ 10 13
g g
poise. Had this been a crystalline material, the expansion curve would
have ended abruptly at the melting point of the solid as it turned into
a nonviscous liquid. As the measurement of the glass continues, a
point is reached where, under the conditions of the instrument,
expansion stops and the sample begins to contract. This point is called
the dilatometric softening point T of the glass. For the conditions of
d
Amtir C1 thermal expansion (annealed, rise 0.5°C/min)
300
2004.06.09 (56.50 mm)
Annealed T ~ 154°C
d
250
–5
α (25–75) = 2.27 × 10 /°C
200
Expansion (µm) 150 α (25–100) = 2.31 × 10 /°C T ~ 133°C
–5
g
–5
α (25–125) = 2.43 × 10 /°C
100
50
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2.2 Measurement of thermal expansion and glass transition
temperature for AMI C1 glass.