Page 392 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 392
370 CONSEQUENCES OF CORROSION
90 μm
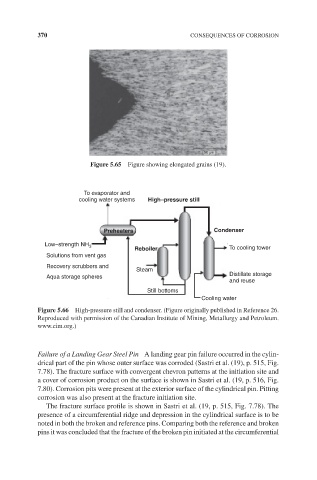
Figure 5.65 Figure showing elongated grains (19).
To evaporator and
cooling water systems High–pressure still
Preheaters Condenser
Low–strength NH 3
Reboiler To cooling tower
Solutions from vent gas
Recovery scrubbers and
Steam
Aqua storage spheres Distillate storage
and reuse
Still bottoms
Cooling water
Figure 5.66 High-pressure still and condenser. (Figure originally published in Reference 26.
Reproduced with permission of the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum.
www.cim.org.)
Failure of a Landing Gear Steel Pin A landing gear pin failure occurred in the cylin-
drical part of the pin whose outer surface was corroded (Sastri et al. (19), p. 515, Fig.
7.78). The fracture surface with convergent chevron patterns at the initiation site and
a cover of corrosion product on the surface is shown in Sastri et al. (19, p. 516, Fig.
7.80). Corrosion pits were present at the exterior surface of the cylindrical pin. Pitting
corrosion was also present at the fracture initiation site.
The fracture surface profile is shown in Sastri et al. (19, p. 515, Fig. 7.78). The
presence of a circumferential ridge and depression in the cylindrical surface is to be
noted in both the broken and reference pins. Comparing both the reference and broken
pins it was concluded that the fracture of the broken pin initiated at the circumferential