Page 102 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 102
74 TRANSFER OF SOLIDS
and bulk density is due to Gerchow (1980) and is
R/min
Line length
(ft) 55 Ib/cuft 55-85 85-115
200 4000 5000 6000
500 5000 6000 7000
1000 6000 7000 8000
Conveying capacity expressed as vol % of solids in the stream
usually is well under 5 ~01%. From Table 5.1, for example, it is
about 1.5% for alumina and 6.0% for polystyrene pellets, figured at
atmospheric pressure; at 12 psig these percentages will be roughly
doubled, and at subatmospheric pressures they will be lower.
POWER CONSUMPTION AND PRESSURE DROP
The power consumption is made up of the work of compression of
the air and the frictional losses due to the flows of air and solid
through the line. The work of compression of air at a flow rate rnL
and CJC, = 1.4 is given by
w, = 3.5(53.3)(7‘ + 460)rn~[(P2/P1)0~2s57 11 (ft lbf/sec)
-
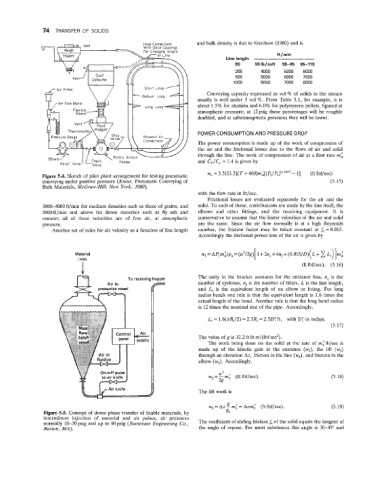
Figure 5.4. Sketch of pilot plant arrangement for testing pneumatic
conveying under positive pressure (Kraus, Pneumatic Conveying of (5.15)
Bulk Materials, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1980).
with the flow rate in lb/sec.
Frictional losses are evaluated separately for the air and the
3000-4000 ft/min for medium densities such as those of grains, and solid. To each of these, contributions are made by the line itself, the
5000ft/min and above for dense materials such as fly ash and elbows and other fittings, and the receiving equipment. It is
cement; all of these velocities are of free air, at atmospheric conservative to assume that the linear velocities of the air and solid
pressure. are the same. Since the air flow normally is at a high Reynolds
Another set of rules for air velocity as a function of line length number, the friction factor may be taken constant at fa = 0.015.
Accordingly the frictional power loss of the air is given by
-
[
Material w,=APlrnL/p,= (u2/2g) 1+2n,+4nf+(0.015/D)(L+c Li)]rnL
inlet
1 (ft lbf/sec). (5.16)
rCI To receiving hopper The unity in the bracket accounts for the entrance loss, n, is the
Air to number of cyclones, nf is the number of filters, L is the line length,
pressurize vessel and Lt is the equivalent length of an elbow or fitting. For long
radius bends one rule is that the equivalent length is 1.6 times the
actual length of the bend. Another rule is that the long bend radius
is 12 times the nominal size of the pipe. Accordingly,
Li = 1.6(nRj/2) = 2.5Rj = 2.5D;ft, with D; in inches.
(5.17)
The value of g is 32.2 ft lb m/(lbf sec’).
The work being done on the solid at the rate of rnflblsec is
made up of the kinetic gain at the entrance (w2), the lift (w,)
through an elevation Az, friction in the line (w4), and friction in the
elbow (w5). Accordingly,
w --mi (ft lbf/sec). (5.18)
UZ
2-2g
Air knife The lift work is
g
w, = Az - rn,‘ = Azrn,’ (ft lbf/sec). (5.19)
Figure 5.5. Concept of dense phase transfer of friable materials, by gc
intermittent injection of material and air pulses, air pressures
normally 10-30 psig and up to 90 psig (Sturtevant Engineering Co., The coefficient of sliding friction f, of the solid equals the tangent of
Boston, MA). the angle of repose. For most substances this angle is 30-45” and