Page 217 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 217
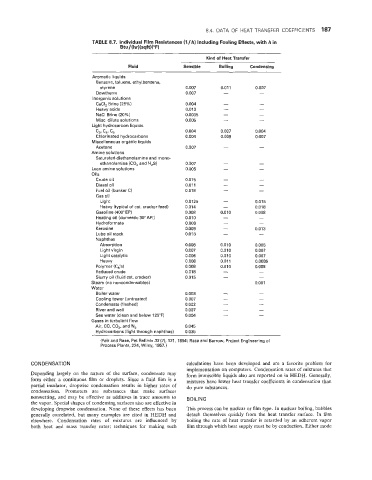
8.4. DATA OF HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENTS 487
TABLE 8.7. Individual Film Resistances (l/h) Including Fouling Effects, with h in
Btu/(hr)(sqWF)
Kind of Heat Transfer
Fluid Sensible Boiling Condensing
Aromatic liquids
Benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene,
styrene 0.007 0.007
Dowtherm 0.007 -
lnorganic solutions
CaCI, Brine (25%) 0.004 -
Heavy acids 0.013 -
NaCl Brine (20%) 0.0035 -
Misc. dilute solutions 0.005 -
Light hydrocarbon liquids
c,, c,. C, 0.004 0.004
Chlorinated hydrocarbons 0.004 0.007
Miscellaneous organic liquids
Acetone 0.007 -
Amine solutions
Saturated dicthanolamine and mono-
ethanolamine (CO, and H,S) 0.007 -
Lean amine solutions 0.005 -
Oils
Crude oil 0.015 -
Diesel oil 0.01 1 -
Fuel oil (bunker C) 0.018 -
Gas oil
Lighl 0.0125 0.015
Heavy (typical of cat. cracker feed) 0.014 0.018
Gasoline (408" EP) 0.008 0.008
Heating oil (domestic 30" API) 0.010 -
Hydroformate 0.006 -
Kerosine 0.009 0.013
Lube oil stock 0.018 -
Naphthas
Absorption 0.008 0.006
Light virgin 0.007 0.007
Light catalytic 0.006 0.007
Heavy 0.008 0.0085
Polymer (C,'s) 0.008 0.008
Reduced crude 0.018 -
Slurry oil (fluid cat. cracker) 0.015 -
Steam (no noncondensables) 0.001
Water
Boiler water 0.003 -
Cooling tower (untreated) 0.007 -
Condensate (flashed) 0.002 -
River and well 0.007 -
Sea water (clean and below 125°F) 0.004 -
Gases in turbulent flow
Air, CO, CO,, and N, 0.045
Hvdrocarbok Lliahithrouah naohthas) 0.035
~~ ~ ~
(Fair and Rase, Pet Refiner 33(7), 121, 1854; Rase and Barrow, Project Engineering of
Process Plants, 224, Wiley, 1957.)
60 N DENSATI 0 N calculations have been developed and are a favorite problem for
implementation on computers. Condensation rates of mixtures that
Depending largely on the nature of the surface, condensate may form immiscible liquids also are reported on in HEDR. Generally,
form either a continuous film or droplets. Since a fluid film is a mixtures have lower heat transfer coefficients in condensation than
partial insulator, dropwise condensation results in higher rates of do pure substances.
condensation. Promoters are substances that make surfaces
nonwetting, and may be effective as additives in trace amounts to BOILING
the vapor. Special shapes of condensing surfaces also are effective in
developing dropwise condensation. None of these effects has been This process can be nuclear or film type. In nuclear boiling, bubbles
generally correlated, but many examples are cited in HEDH and detach themselves quickly from the heat transfer surface. In film
elsewhere. Condensation rates of mixtures are influenced by boiling the rate of heat transfer is retarded by an adherent vapor
both heat anti mass transfer rates; techniques for making such film through which heat supply must be by conduction. Either mode