Page 275 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 275
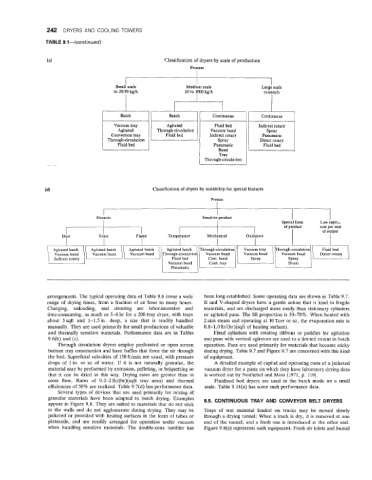
242 DRYERS AND COOLING TOWERS
TABLE 9.1-(continued)
Classification of dryers by scale of production
Process
Smali scale Medium scale Largi scale
to 20/50 kg/h 50 to lo00 kg/h tonnes/h
I I I
Vacuum tray Agitated Fluid bed Indirect rotary
Agitated Through-circulation Vacuum band
Convection tray Fluid bed Indirect rotary Pneumatic
Through-circulation Spray Direct rotary
Fluid bed Pneumatic Fluid bed
Band
Tray
Through-circulation
Classification of dryers by suitability for special features
Hazards Sensitive product
arrangements. The typical operating data of Table 9.6 cover a wide been long established. Some operating data are shown in Table 9.7.
range of drying times, from a fraction of an hour to many hours. It and V-shaped dryers have a gentle action that is kind to fragile
Charging, unloading, and cleaning are labor-intensive and materials, and are discharged more easily than stationary cylinders
time-consuming, as much as 5-6 hr for a 200-tray dryer, with trays or agitated pans. The fill proportion is 50-70%. When heated with
about Ssqft and 1-1.5in. deep, a size that is readily handled 2 atm steam and operating at 10 Torr or so, the evaporation rate is
manually. They are used primarily for small productions of valuable 0.8-1.0 Ib/(hr)(sqft of heating surface).
and thermally sensitive materials. Performance data are in Tables Fixed cylinders with rotating ribbons or paddles for agitation
9.6(b) and (c). and pans with vertical agitators are used to a limited extent in batch
Through circulation dryers employ perforated or open screen operation. Pans are used primarily for materials that become sticky
bottom tray construction and have baffles that force the air through during drying. Table 9.7 and Figure 9.7 are concerned with this kind
the bed. Superficial velocities of 150 ft/min are usual, with pressure of equipment.
drops of lin. or so of water. If it is not naturally granular, the A detailed example of capital and operating costs of a jacketed
material may be preformed by extrusion, pelleting, or briquetting so vacuum dryer for a paste on which they have laboratory drying data
that it can be dried in this way. Drying rates are greater than in is worked out by Nonhebel and Moss (1971, p. 110).
cross flow. Rates of 0.2-2lb/(hr)(sqft tray area) and thermal Fluidized bed dryers are used in the batch mode on a small
efficiencies of 50% are realized. Table 9.7(d) has performance data. scale. Table 9.14(a) has some such performance data.
Several types of devices that are used primarily for mixing of
granular materials have been adapted to batch drying. Examples 9.5. CONTINUOUS TRAY AND CONVEYOR BELT DRYERS
appear in Figure 9.8. They are suited to materials that do not stick
to the walls and do not agglomerate during drying. They may be Trays of wet material loaded on trucks may be moved slowly
jacketed or provided with heating surfaces in the form of tubes or through a drying tunnel: When a truck is dry, it is removed at one
platecoils, and are readily arranged for operation under vacuum end of the tunnel, and a fresh one is introduced at the other end.
when handling sensitive materials. The double-cone tumbler has Figure 9.8(c) represents such equipment. Fresh air inlets and humid