Page 312 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 312
276 DRYERS AND COOLING TOWERS
TABLE 9.17. Particle Diameters, Densities, and Energy orifice diameters are 0.012-0.15 in. An acceptably narrow range of
Requirements droplet sizes can be made for a feed of particular physical properties
by adjustment of pressure and diameter. Multiple nozzles are used
(a) Atomizer Performance
for atomization in large diameter towers. Because of the expense of
Power Input motive air or steam, pneumatic nozzles are used mostly in small
Type Size Range (pm) (kWh/1000 L) installations such as pilot plants, but they are most suitable for
dispersion of stringy materials such as polymers and fibers. The
Single fluid nozzle 8-800 0.3-0.5 droplet size increases as the motive pressure is lessened, the range
Pneumatic nozzle 3-250 of 60-1OOpsi being usual. The action of a rotating wheel is
Spray wheel 2-550 0.8-1 .O indicated in Figure 9.14(e). Many different shapes of orifices and
Rotating cup 25-950
vanes are used for feeds of various viscosities, erosiveness, and
clogging tendencies. Operating conditions are up to 60,000 lb/hr per
(b) Dry Product Size Range atomizer, speeds up to 20,00Orpm, and peripheral speeds of
250-600 ft/sec.
Product vm The main variables in the operation of atomizers are feed
pressure, orifice diameter, flow rate and motive pressure for nozzles
Skim milk 20-250
Coffee 50-600 and geometry and rotation speed of wheels. Enough is known about
Eggs 5-500 these factors to enable prediction of size distribution and throw
Egg white 1-40 of droplets in specific equipment. Effects of some atomizer
Color pigments 1-50 characteristics and other operating variables on spray dryer
Detergents 20-2000 performance are summarized in Table 9.18. A detailed survey of
Ceramics 15-500 theory, design and performance of atomizers is made by Masters
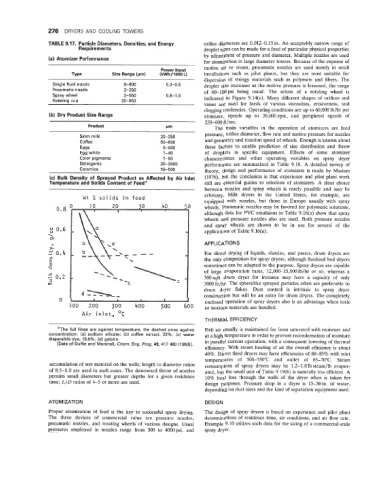
(c) Bulk Density of Sprayed Product as Affected by Air Inlet (1976), but the conclusion is that experience and pilot plant work
Temperature and Solids Content of Feed" still are essential guides to selection of atomizers. A clear choice
between nozzles and spray wheels is rarely possible and may be
arbitrary. Milk dryers in the United States, for example, are
equipped with nozzles, but those in Europe usually with spray
0.8 wheels. Pneumatic nozzles may be favored for polymeric solutions,
although data for PVC emulsions in Table 9.16(a) show that spray
wheels and pressure nozzles also are used. Both pressure nozzles
and spray wheels are shown to be in use for several of the
; 0.6 applications of Table 9.16(a).
\
Is)
APPLICATIONS
9,
.: >. 0.4 For direct drying of liquids, slurries, and pastes, drum dryers are
In the only competition for spray dryers, although fluidized bed dryers
c
P) sometimes can be adapted to the purpose. Spray dryers are capable
-0
Y of large evaporation rates, 12,000-15,000 lb/hr or so, whereas a
- 0.2 300sqft drum dryer for instance may have a capacity of only
2
m 3000 lb/hr. The spherelike sprayed particles often are preferable to
d L - I drum dryer flakes. Dust control is intrinsic to spray dryer
construction but will be an extra for drum dryers. The completely
0 1 I I enclosed operation of spray dryers also is an advantage when toxic
100 200 300 400 500 600 or noxious materials are handled.
Air inlet, OC
THERMAL EFFICIENCY
'The full lines are against temperature, the dashed ones against Exit air usually is maintained far from saturated with moisture and
concentration: (a) sodium silicate; (b) coffee extract, 22%; (c) water at a high temperature in order to prevent recondensation of moisture
dispersible dye, 19.5%; (d) gelatin. in parallel current operation, with a consequent lowering of thermal
[Data of Duffie and Marshall, Chem. Eng. Prog. 49, 417 480 (1953)l.
efficiency. With steam heating of air the overall efficiency is about
40%. Direct fired dryers may have efficiencies of 8045% with inlet
temperatures of 500-550°C and outlet of 65-70°C. Steam
accumulation of wet material on the walls; length to diameter ratios consumption of spray dryers may be 1.2-1.8 lb steam/lb evapor-
of 0.5-1.0 are used in such cases. The downward throw of nozzles ated, but the small unit of Table 9.19(b) is naturally less efficient. A
permits small diameters but greater depths for a given residence 10% heat loss through the walls of the dryer often is taken for
time; LID ratios of 4-5 or more are used. design purposes. Pressure drop in a dryer is 15-50in. of water,
depending on duct sizes and the kind of separation equipment used.
ATOMIZATION DESIGN
Proper atomization of feed is the key to successful spray drying. The design of spray dryers is based on experience and pilot plant
The three devices of commercial value are pressure nozzles, determinations of residence time, air conditions, and air flow rate.
pneumatic nozzles, and rotating wheels of various designs. Usual Example 9.10 utilizes such data for the sizing of a commercial scale
pressures employed in nozzles range from 300 to 4000psi, and spray dryer.