Page 102 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 102
Speight_Part II_A 11/7/01 3:16 PM Page 2.43
ALUMINA 2.43
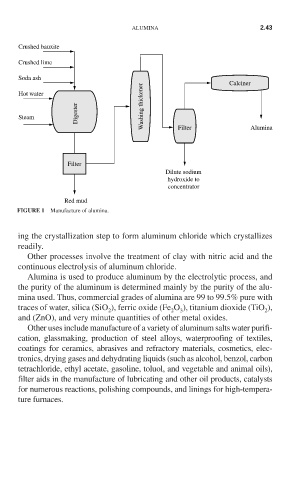
Crushed bauxite
Crushed lime
Soda ash
Calciner
Hot water
Digester Washing thickener
Steam Filter Alumina
Filter
Dilute sodium
hydroxide to
concentrator
Red mud
FIGURE 1 Manufacture of alumina.
ing the crystallization step to form aluminum chloride which crystallizes
readily.
Other processes involve the treatment of clay with nitric acid and the
continuous electrolysis of aluminum chloride.
Alumina is used to produce aluminum by the electrolytic process, and
the purity of the aluminum is determined mainly by the purity of the alu-
mina used. Thus, commercial grades of alumina are 99 to 99.5% pure with
traces of water, silica (SiO ), ferric oxide (Fe O ), titanium dioxide (TiO ),
2
2
2
3
and (ZnO), and very minute quantities of other metal oxides.
Other uses include manufacture of a variety of aluminum salts water purifi-
cation, glassmaking, production of steel alloys, waterproofing of textiles,
coatings for ceramics, abrasives and refractory materials, cosmetics, elec-
tronics, drying gases and dehydrating liquids (such as alcohol, benzol, carbon
tetrachloride, ethyl acetate, gasoline, toluol, and vegetable and animal oils),
filter aids in the manufacture of lubricating and other oil products, catalysts
for numerous reactions, polishing compounds, and linings for high-tempera-
ture furnaces.