Page 142 - Chemical engineering design
P. 142
122
For complex networks a more general expression is needed to determine the minimum
number of exchangers: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
0
0
Z min D N C L S 3.42
0
where L D the number of internal loops present in the network
S D the number of independent branches (subsets) that exist in the network.
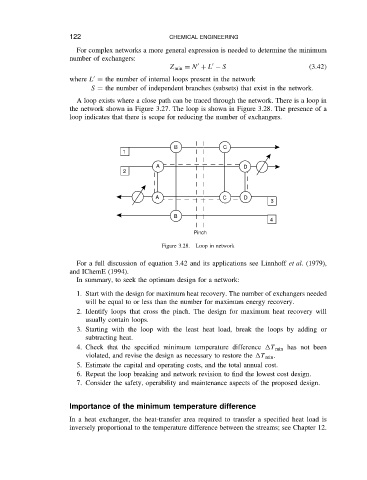
A loop exists where a close path can be traced through the network. There is a loop in
the network shown in Figure 3.27. The loop is shown in Figure 3.28. The presence of a
loop indicates that there is scope for reducing the number of exchangers.
B C
1
A D
2
A C D
3
B
4
Pinch
Figure 3.28. Loop in network
For a full discussion of equation 3.42 and its applications see Linnhoff et al. (1979),
and IChemE (1994).
In summary, to seek the optimum design for a network:
1. Start with the design for maximum heat recovery. The number of exchangers needed
will be equal to or less than the number for maximum energy recovery.
2. Identify loops that cross the pinch. The design for maximum heat recovery will
usually contain loops.
3. Starting with the loop with the least heat load, break the loops by adding or
subtracting heat.
4. Check that the specified minimum temperature difference T min has not been
violated, and revise the design as necessary to restore the T min .
5. Estimate the capital and operating costs, and the total annual cost.
6. Repeat the loop breaking and network revision to find the lowest cost design.
7. Consider the safety, operability and maintenance aspects of the proposed design.
Importance of the minimum temperature difference
In a heat exchanger, the heat-transfer area required to transfer a specified heat load is
inversely proportional to the temperature difference between the streams; see Chapter 12.