Page 143 - Chemical engineering design
P. 143
123
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES
This means that the value chosen for T min will determine the size of the heat
exchangers in a network. Reducing T min will increase the heat recovery, decreasing
the utility consumption and cost, but at the expense of an increase in the exchanger size
and capital cost.
For any network there will be a best value for the minimum temperature difference
that will give the lowest total annual costs. The effect of changes in the specified T min
need to be investigated when optimising a heat recovery system.
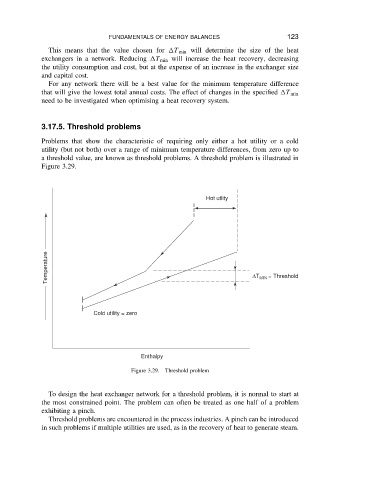
3.17.5. Threshold problems
Problems that show the characteristic of requiring only either a hot utility or a cold
utility (but not both) over a range of minimum temperature differences, from zero up to
a threshold value, are known as threshold problems. A threshold problem is illustrated in
Figure 3.29.
Hot utlity
Temperature ∆T MIN = Threshold
Cold utility = zero
Enthalpy
Figure 3.29. Threshold problem
To design the heat exchanger network for a threshold problem, it is normal to start at
the most constrained point. The problem can often be treated as one half of a problem
exhibiting a pinch.
Threshold problems are encountered in the process industries. A pinch can be introduced
in such problems if multiple utilities are used, as in the recovery of heat to generate steam.