Page 208 - Chemical engineering design
P. 208
FLOW-SHEETING
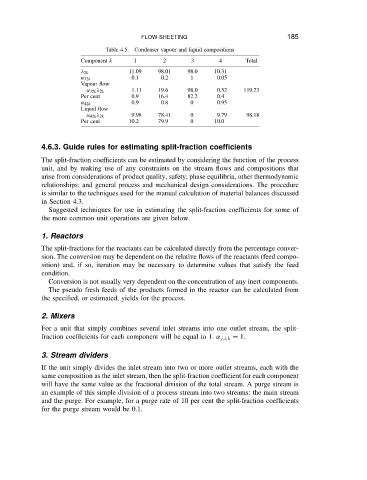
Table 4.5.
2
3
4
Component k 1 Condenser vapour and liquid compositions Total 185
2k 11.09 98.01 98.0 10.31
˛ 32k 0.1 0.2 1 0.05
Vapour flow
˛ 32k 2k 1.11 19.6 98.0 0.52 119.23
Per cent 0.9 16.4 82.2 0.4
˛ 42k 0.9 0.8 0 0.95
Liquid flow
˛ 42k 2k 9.98 78.41 0 9.79 98.18
Per cent 10.2 79.9 0 10.0
4.6.3. Guide rules for estimating split-fraction coefficients
The split-fraction coefficients can be estimated by considering the function of the process
unit, and by making use of any constraints on the stream flows and compositions that
arise from considerations of product quality, safety, phase equilibria, other thermodynamic
relationships; and general process and mechanical design considerations. The procedure
is similar to the techniques used for the manual calculation of material balances discussed
in Section 4.3.
Suggested techniques for use in estimating the split-fraction coefficients for some of
the more common unit operations are given below.
1. Reactors
The split-fractions for the reactants can be calculated directly from the percentage conver-
sion. The conversion may be dependent on the relative flows of the reactants (feed compo-
sition) and, if so, iteration may be necessary to determine values that satisfy the feed
condition.
Conversion is not usually very dependent on the concentration of any inert components.
The pseudo fresh feeds of the products formed in the reactor can be calculated from
the specified, or estimated, yields for the process.
2. Mixers
For a unit that simply combines several inlet streams into one outlet stream, the split-
fraction coefficients for each component will be equal to 1. ˛ j,i,k D 1.
3. Stream dividers
If the unit simply divides the inlet stream into two or more outlet streams, each with the
same composition as the inlet stream, then the split-fraction coefficient for each component
will have the same value as the fractional division of the total stream. A purge stream is
an example of this simple division of a process stream into two streams: the main stream
and the purge. For example, for a purge rate of 10 per cent the split-fraction coefficients
for the purge stream would be 0.1.