Page 222 - Chemical engineering design
P. 222
(f) PIPING AND INSTRUMENTATION (g) 199
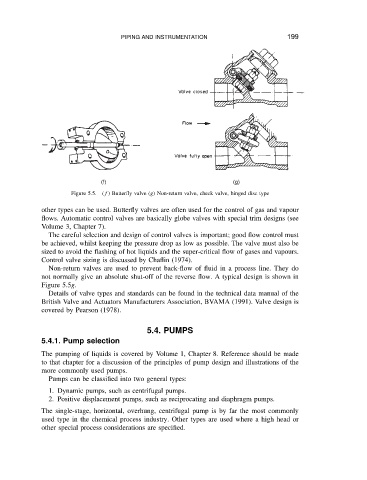
Figure 5.5. (f) Butterfly valve (g) Non-return valve, check valve, hinged disc type
other types can be used. Butterfly valves are often used for the control of gas and vapour
flows. Automatic control valves are basically globe valves with special trim designs (see
Volume 3, Chapter 7).
The careful selection and design of control valves is important; good flow control must
be achieved, whilst keeping the pressure drop as low as possible. The valve must also be
sized to avoid the flashing of hot liquids and the super-critical flow of gases and vapours.
Control valve sizing is discussed by Chaflin (1974).
Non-return valves are used to prevent back-flow of fluid in a process line. They do
not normally give an absolute shut-off of the reverse flow. A typical design is shown in
Figure 5.5g.
Details of valve types and standards can be found in the technical data manual of the
British Valve and Actuators Manufacturers Association, BVAMA (1991). Valve design is
covered by Pearson (1978).
5.4. PUMPS
5.4.1. Pump selection
The pumping of liquids is covered by Volume 1, Chapter 8. Reference should be made
to that chapter for a discussion of the principles of pump design and illustrations of the
more commonly used pumps.
Pumps can be classified into two general types:
1. Dynamic pumps, such as centrifugal pumps.
2. Positive displacement pumps, such as reciprocating and diaphragm pumps.
The single-stage, horizontal, overhung, centrifugal pump is by far the most commonly
used type in the chemical process industry. Other types are used where a high head or
other special process considerations are specified.