Page 223 - Chemical engineering design
P. 223
200
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Pump selection is made on the flow rate and head required, together with other process
considerations, such as corrosion or the presence of solids in the fluid.
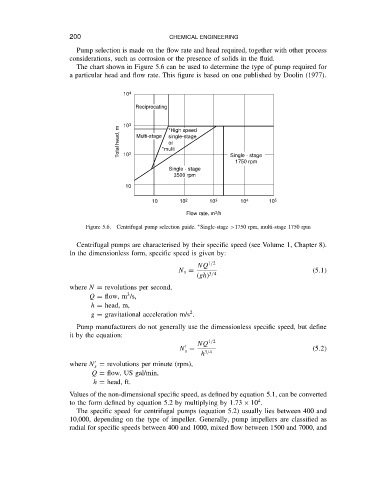
The chart shown in Figure 5.6 can be used to determine the type of pump required for
a particular head and flow rate. This figure is based on one published by Doolin (1977).
10 4
Reciprocating
Total head, m 10 3 Multi-stage *multi
*High speed
single-stage
or
2
10
Single - stage
1750 rpm
Single - stage
3500 rpm
10
10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5
3
Flow rate, m /h
Ł
Figure 5.6. Centrifugal pump selection guide. Single-stage >1750 rpm, multi-stage 1750 rpm
Centrifugal pumps are characterised by their specific speed (see Volume 1, Chapter 8).
In the dimensionless form, specific speed is given by:
NQ 1/2
N s D 5.1
gh 3/4
where N D revolutions per second,
3
Q D flow, m /s,
h D head, m,
2
g D gravitational acceleration m/s .
Pump manufacturers do not generally use the dimensionless specific speed, but define
it by the equation:
NQ 1/2
0
N D 5.2
s 3/4
h
0
where N D revolutions per minute (rpm),
s
Q D flow, US gal/min,
h D head, ft.
Values of the non-dimensional specific speed, as defined by equation 5.1, can be converted
4
to the form defined by equation 5.2 by multiplying by 1.73 ð 10 .
The specific speed for centrifugal pumps (equation 5.2) usually lies between 400 and
10,000, depending on the type of impeller. Generally, pump impellers are classified as
radial for specific speeds between 400 and 1000, mixed flow between 1500 and 7000, and